A recent vulnerability in Apache Tomcat, identified as CVE-2025-24813, has sparked concerns among cybersecurity professionals due to its potential for exploitation in unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE), severe information leakage, and malicious content injection.
This vulnerability was publicly disclosed on March 10, 2025, along with a patch, and has already seen initial exploit attempts by attackers probing vulnerable servers for weaknesses.
Understanding CVE-2025-24813
CVE-2025-24813 pertains to a path equivalence vulnerability in Apache Tomcat, a widely used open-source web server and Java servlet container.
The vulnerability affects how Tomcat processes file paths internally. Although Apache has labeled this vulnerability as moderate severity due to specific exploitation prerequisites, it poses serious risks if exploited, including RCE, which can compromise server integrity and confidentiality.
The exploitation of CVE-2025-24813 requires several non-default conditions:
- Default Servlet Write Capability: This must be explicitly enabled, which is not the case by default.
- Partial PUT Requests: These must be allowed.
- File-Based Session Persistence: The web application must use this with default storage locations.
- Deserialization Vulnerable Library: Such a library must be present for the payload to execute via deserialization.
- Internal File Naming Knowledge: Attackers need to understand the target server’s internal file naming conventions and directory structure.
Despite these prerequisites, the vulnerability’s potential impact warrants immediate action to patch or mitigate it.
Observed Attack Traffic
Akamai’s Security Intelligence Group reported observing attack traffic mere days after the vulnerability was disclosed.
Most attack payloads aimed to probe potential servers for vulnerabilities, with a notable focus on targeting .session file paths.

These attacks involved uploading malicious Java serialized objects, which could result in malicious payloads being executed upon deserialization.
Common Attack Variants
- Session File Targets: Attackers specifically target .session files, using a randomized naming scheme, appending a six-character base with the .session file extension.
- Java Serialized Objects: Malicious objects, often involving java.net.URL, are used to “call home” after deserialization, indicating successful exploitation.
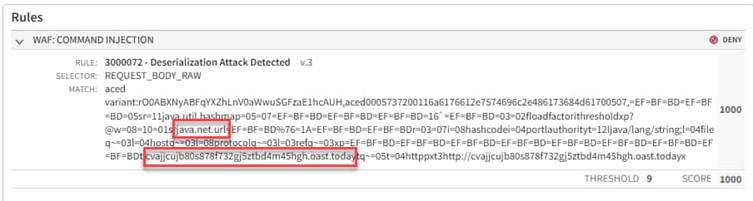

Identifying vulnerable Apache Tomcat instances can be challenging due to its widespread integration across various applications, including indirect dependencies. Here are some detection methods:
- Recursive Scanning: Look for tomcat-api.jar files, which indicate Tomcat presence.
- Version Assessment: Extract the version from the JAR manifest and compare it against known vulnerable versions (11.0.0-M1 to 11.0.2, 10.1.0-M1 to 10.1.34, 9.0.0-M1 to 9.0.98).
- Akamai Guardicore Insight Query: Utilize specific queries to identify vulnerable assets.
Mitigation Steps
Update to the latest versions that fix the vulnerability: Apache Tomcat versions 11.0.3, 10.1.35, and 9.0.99.
- Akamai App & API Protector: An Adaptive Security Engine Rapid Rule (3000957) has been deployed to detect and block CVE-2025-24813 exploits.
- Configurations: Ensure the default servlet’s write capability is disabled and restrict partial PUT requests.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor for suspicious traffic patterns, especially those targeting .session files.
While CVE-2025-24813 is considered moderate in severity due to its specific prerequisites, its potential for severe impact if exploited necessitates prompt action.
Organizations must prioritize updating Apache Tomcat versions and implementing protective measures to safeguard against these threats.
By taking proactive steps in detection and mitigation, organizations can effectively protect themselves from emerging threats like CVE-2025-24813, ensuring the security and integrity of their systems and data.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links & Phishing Attacks With Threat Intelligence Lookup - Try for Free
