An information stealer malware dubbed “VectorStealer”, which possesses the ability to pilfer precious .rdp files, was detected by Cyble researchers.
Cybercriminals often use information stealers to commit identity theft and financial fraud. The act of stealing allows malicious individuals to perform RDP hijackings, as the stolen files contain the key to accessing RDP sessions, including all crucial information necessary for remote control.
Information stealers are widely used to steal sensitive information from computers and other devices. They can capture and exfiltrate sensitive data such as passwords, credit card numbers, banking information, and other confidential information without the user’s knowledge or consent.
VectorStealer: a new information stealer on the market
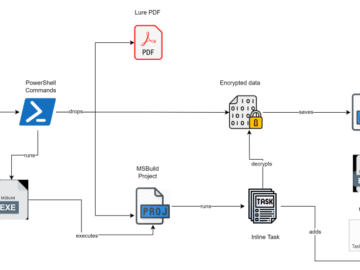
VectorStealer surfaced on cybercrime forums in the latter half of 2022. The threat actor (TA) behind this stealer primarily operates through a web panel and a Telegram channel.
According to the report, the VectorStealer has the capability to recover sensitive information from all major browsers, including Firefox, Chrome, and Safari.
The stealer is also capable of stealing Discord tokens and sensitive files, as well as gathering basic information about the infected computer. The payload of the stealer is being sold for 63 USD in Bitcoin.
The stealer payload can be generated through the web panel, which allows the attacker to create custom malware without having advanced programming skills. The web panel has a user-friendly interface and provides various options for customization, such as specifying the actions the malware will perform and configuring the behavior of the malware.
The sensitive information stolen from the victim’s system can be exfiltrated using SMTP, Discord, and Telegram. Interestingly, on the same web panel, the TA advertises KGB Crypter and claims that this crypter can kill multiple antivirus solutions.
Crypters are tools used by threat actors to evade detection by encrypting the malware code, making it difficult for antivirus software to identify and remove it.
The threat actors behind KGB Crypter provide the service through their website and claim that it is compatible with .Net and C++-based binaries. They also claim that multiple prominent malware families, such as Redline, Quasar RAT, Venom RAT, and Pandora RAT, are already using this crypter.
The creators of KGB Crypter are of Russian origin and boast that over 1,000 users have registered on their site, indicating its popularity among TAs.
The crypter is offered as a paid service for 145 USD per month and is equipped with a metamorphic generator, which alters the code each time it is compiled, making it more challenging for antivirus software to detect.
VectorStealer and KGB Crypter pose a significant threat to online security and sensitive information. Individuals and organizations must take precautions to protect their systems and sensitive data, such as keeping the software and security tools up-to-date, avoiding suspicious emails and links, and only downloading apps from reputable sources.
VectorStealer: How do Information stealers work?
Information stealers like VectorStealer typically work by infiltrating a device, such as a computer or mobile device, and then actively monitoring the system for sensitive information. They may use various techniques to achieve this, such as keylogging, screen capture, or data scraping.
Once the information stealer has obtained the desired data, it can exfiltrate it to a remote server controlled by the attacker, where it can be used for malicious purposes, such as identity theft or financial fraud.
Information stealers can be delivered to a device through various methods, including email attachments, malicious websites, and software downloads. They can also be hidden within legitimate software or disguised as harmless apps or programs.
While there is no single fix for protecting oneself from information stealers, the rule of thumb says that one practice safe computing habits, such as keeping the software and security tools up-to-date, avoiding suspicious emails and links, and only downloading apps from reputable sources to reduce the risk of falling victim to an information stealer.
What is RDP hacking?
RDP hacking refers to unauthorized access to a remote desktop protocol (RDP) server, often accomplished through stolen login credentials or exploiting vulnerabilities in the RDP configuration.
This hacking allows an attacker to control a victim’s computer or network remotely, potentially accessing sensitive information, installing malware, or using the compromised system for other malicious purposes.
RDP hacking can have severe consequences for individuals and organizations, and it is essential to secure RDP connections to prevent such attacks.
There are several ways hackers attack RDPs, some of them using brute force attacks, exploiting unsecured RDP connections, injecting malicious RDP software, and man-in-the-middle attacks are still prevalent while attacking an RDP ecosystem.
These are just a few examples of the many ways RDP systems can be hacked, highlighting the importance of secure RDP configurations and practices to prevent such attacks.