A targeted cyber-espionage campaign exploiting Windows Scheduled Tasks and DLL side-loading to deploy the sophisticated ValleyRAT backdoor.
The operation pivots on tailored spear-phishing emails, weaponized Windows shortcuts, and a persistent task scheduler mechanism, all delivering a multi-stage malware payload designed to harvest sensitive intelligence from Chinese FinTech and cryptocurrency firms.
Adversaries behind Operation Silk Lure craft highly convincing emails posing as job applicants and send them to HR and technical hiring teams in Chinese organizations.
Each message includes a malicious .LNK shortcut embedded in a seemingly legitimate résumé PDF.
Seqrite Lab researchers have uncovered Operation Silk Lure,the code reveals its C2 server at 206.119.175.16 and launches the ValleyRAT backdoor.
The decoy résumé is authored in Simplified Chinese to mirror a genuine profile for 李汉兵 (Li Hanbing), a senior full-stack engineer with blockchain and high-frequency trading expertise.
Detailed credentials—such as a bachelor’s degree from South China Agricultural University and work history at Huizhou and Shenzhen tech firms—lend credibility and entice recipients to open the attachment.
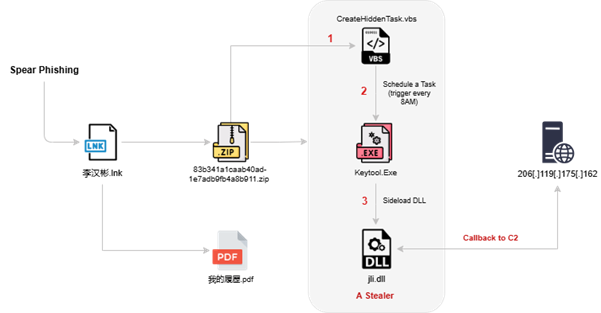
When the victim clicks the .LNK file, the shortcut executes a PowerShell one-liner that reaches out to pan.tenire.com in the United States, downloading key artifacts including keytool.exe, CreateHiddenTask.vbs, jli.dll, and a decoy PDF.
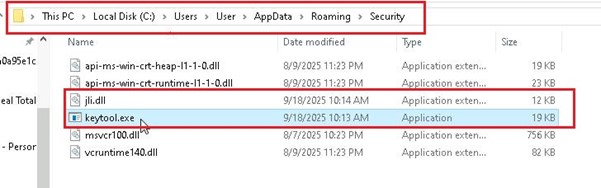
The initial script drops these files into the %APPDATA%Security directory and kicks off the next stage of the attack.
Scheduled Tasks and DLL Side-Loading
Persistence is achieved through a VBScript (CreateHiddenTask.vbs) that programmatically uses COM objects to register a daily scheduled task named “Security.”
When we executed the sample LNK in our secure environment, it downloaded a second-stage payload to C:Users

This task launches keytool.exe every day at 8:00 AM, camouflaged to appear as a Microsoft-signed process. After registering the task, the script self-deletes to erase forensic traces.
At runtime, keytool.exe side-loads jli.dll, reading a hidden, RC4-encrypted payload from its own PE sections. The S-box is seeded with the fixed key “123cba,” decrypting the payload in memory and executing it directly without writing to disk.
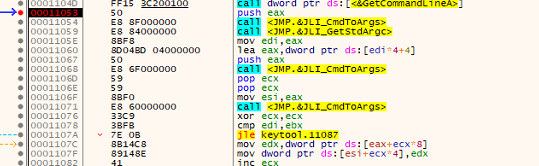

Inside the loader, analysts identified its built-in RC4 routine locating an 8-byte marker (1C3B7EFF1C3B7EFF) to extract the encrypted shellcode.
The second-stage payload, ValleyRAT, initiates extensive reconnaissance, collecting data such as CPU details, user names, screen resolution, clipboard contents, and network information including MAC addresses and open ports.
It probes registry keys to detect VMware or VirtualBox to evade sandbox environments and queries ROOTSecurityCenter2 via WMI to identify installed antivirus products, uninstalling those it finds.
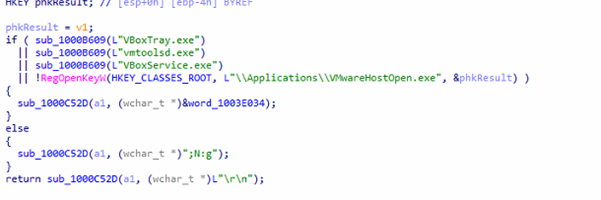

A COM-based task termination routine forcibly disrupts security-software network connections by deleting TCP control blocks associated with Chinese AV vendors like 360Safe and Kingsoft.
ValleyRAT exfiltration functions enable screenshots, keylogging, and file transfer. Commands include plugin installation, filter management, session handling, and self-uninstall triggers.
Sensitive data is encoded and transmitted back to the C2 infrastructure, which spans over 20 domains under a .work TLD cluster on AS133199 (SonderCloud Limited, Hong Kong), designed to mimic job portals and bolster operational resilience.
Implications and Recommendations
Operation Silk Lure leverages China-centric social engineering and advanced persistence mechanisms to infiltrate targeted enterprises.
The campaign’s descriptive moniker—“Silk” for its Chinese footprint, “Lure” for the résumé decoy, “Scheduled Tasks” for its persistence vector, and “DLL Side-Loading” for its loader technique—maps directly to observed artifacts and behaviors.
It collects CPU info, username, screen resolution, port number, uptime, NIC details, MAC, locale, VM check, registry values, and other identifiers.
Organizations should hunt for indicators such as DNS queries to pan.tenire.com, scheduled tasks named “Security,” anomalous PowerShell execution flags (-NoP -ep Bypass), and ImageLoad events involving keytool.exe.
Blocking access to the identified C2 IP range, restricting execution of unsigned VBScript files, and implementing strict application-whitelisting policies can help disrupt this multi-stage threat.
Continuous monitoring for unexpected scheduled tasks and abnormal process launch patterns remains essential to defend against similar campaigns.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.
