Security researcher Henry N. Caga has identified a significant cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability within a Google sub-domain that allows hackers to perform various attacks, including session hijacking, phishing attacks, malware distribution, and data Theft.
This vulnerability exposed a bad actor entry point and highlighted the significance of solid cybersecurity policies.
Free Webinar : Mitigating Vulnerability & 0-day Threats
Alert Fatigue that helps no one as security teams need to triage 100s of vulnerabilities.
:
- The problem of vulnerability fatigue today
- Difference between CVSS-specific vulnerability vs risk-based vulnerability
- Evaluating vulnerabilities based on the business impact/risk
- Automation to reduce alert fatigue and enhance security posture significantly
AcuRisQ, that helps you to quantify risk accurately:
The Discovery
During the investigation, he suspects the URL that associated with https://aihub.cloud.google.com might be vulnerable then he experienced an unsuccessful attempt to exploit the ‘q’ parameter with various payloads, eventually crafting a double-encoded payload that revealed the XSS vulnerability.
Upon realizing the potential severity of the vulnerability, the researcher meticulously documented the process using Burpsuite and crafted a detailed report for Google’s security team. However, the initial report hit a snag when the Google team could not replicate the XSS pop-up.
Undeterred, the researcher delved deeper, creating a bash script to repeatedly request the vulnerable URL, which confirmed the inconsistency of the vulnerability’s trigger.
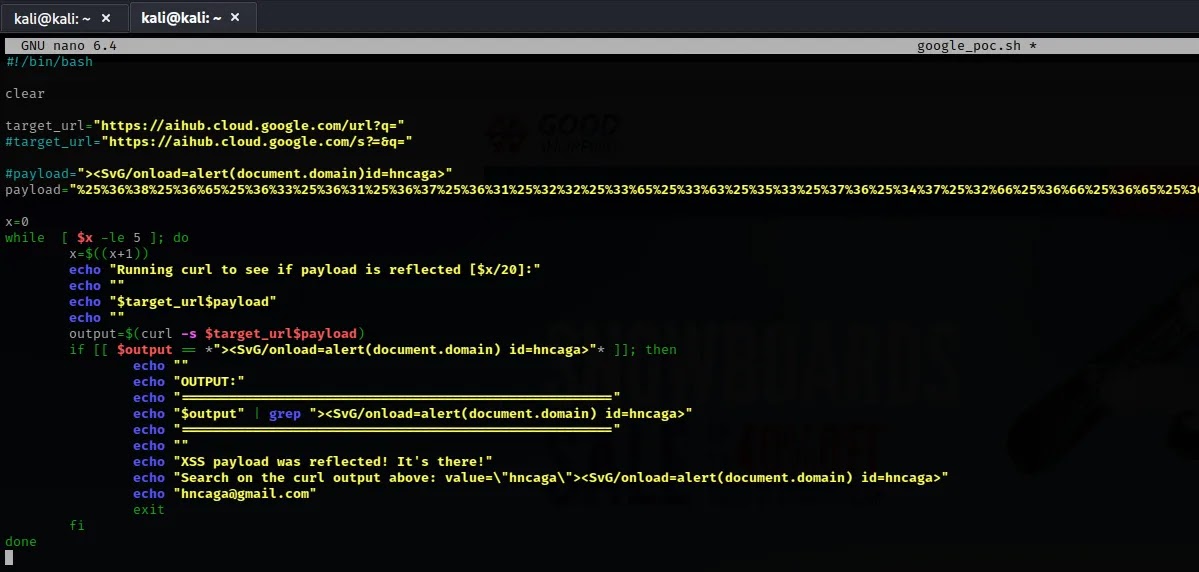
While perusing Google’s subdomains, a particular URL sparked suspicion:
https://aihub.cloud.google.com/url?q=https://cidadesmineradoras.com.br Instinct suggested a potential flaw, prompting an investigation.
The researcher began testing various payloads on the ‘q’ parameter, focusing on a favored XSS payload:
">Despite encoding the payload to bypass potential filters, initial attempts were ineffective.
Persistence led to double encoding the payload, a technique that, surprisingly, triggered the XSS vulnerability.

The moment of success was captured via a Burpsuite-recorded video.
Further investigation revealed that the XSS vulnerability was not isolated to a single URL but affected all URLs from the aihub.cloud.google.com domain when the ‘q’ parameter was appended.
Reporting and Resolution
Adhering to responsible disclosure protocols, the researcher promptly reported the expanded findings to Google’s security team.
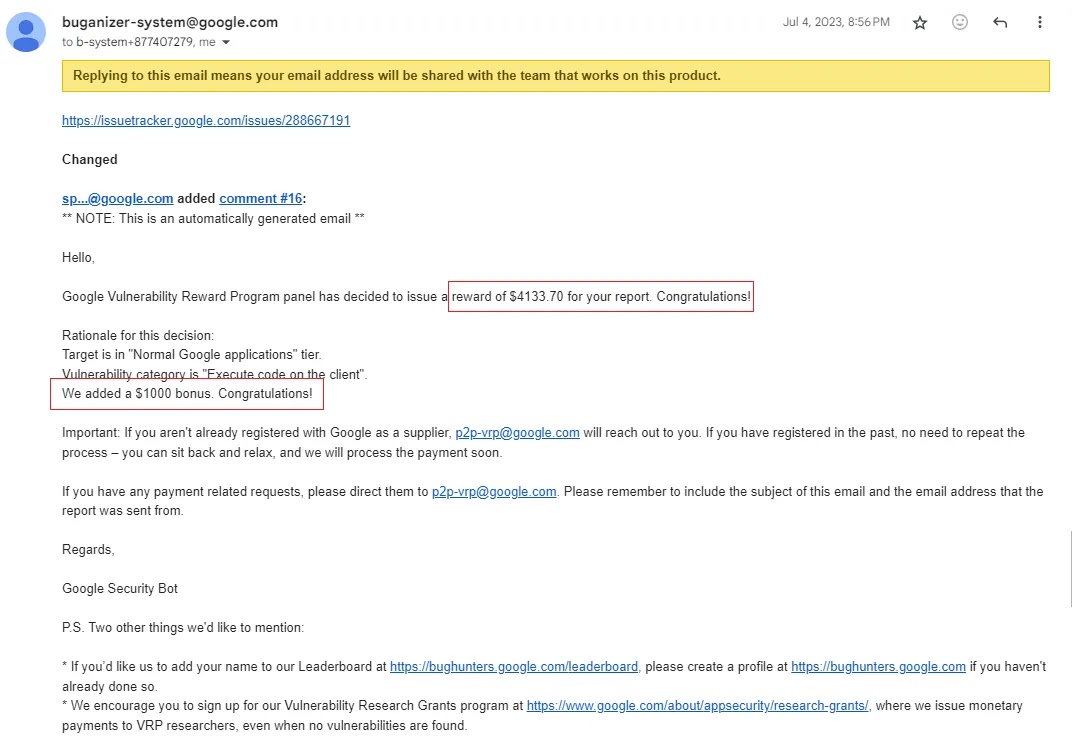
The team responded quickly, upgrading the issue’s priority and severity levels and expressing appreciation for the “Nice Catch!” The researcher was rewarded $4,133.70, including a $1,000 bonus for their comprehensive report and proof of concept scripts.
The Impact
The XSS vulnerability posed significant risks, including:
- Session Hijacking: Attackers could have exploited the vulnerability to take over user sessions.
- Phishing Attacks: The flaw could have facilitated the creation of phishing pages to deceive users.
- Malware Distribution: Users could have been redirected to malware-laden sites.
- Data Theft: Sensitive data like cookies and tokens were at risk of theft.
- Reputation Damage: Such security lapses could harm Google’s reputation for secure services.
The incident reminds us of the persistent need for robust cybersecurity measures, even within the infrastructure of technology leaders like Google. The collaborative efforts of users, developers, and security professionals are crucial in maintaining a secure online environment.
Acknowledgment
The researcher expressed gratitude to Google’s security team for their prompt and professional handling of the vulnerability, which ensured the continued protection of users worldwide.
On March 15, 2024, the researcher received an update from the Google security team informing me that the vulnerability had been resolved. However, the site began returning a 502 error, which Google clarified was due to the deprecation of aihub and its migration to Vertex AI since January 2024.
Are you from SOC and DFIR Teams? – Analyse Malware Incidents & get live Access with ANY.RUN -> Start Now for Free.
