Kaspersky recently reported that a number of iPhones connected to its network were compromised through an iOS vulnerability.
The attackers exploited iMessage’s zero-click exploits, allowing them to install malware on the devices without any user interaction.
Through the exploitation of a vulnerability, a message is delivered in a manner that triggers code execution without the need for user involvement.
Consequently, this exploit enables the automatic download of further malicious content from the server under the attacker’s control.
Following the incident, the message and its attachment are swiftly erased from the device, leaving no trace.
However, the payload itself remains, operating with elevated root privileges. Its purpose is to gather vital system and user data while simultaneously executing commands issued by the attackers.
Since 2019, Kaspersky has been tracking an ongoing campaign called “Operation Triangulation,” which continues to pose threats.
While besides this, Kaspersky also encourages individuals with relevant information about the campaign to come forward and share their knowledge and findings to gather more insights.
Zero-Click iOS Malware Activity
To generate iOS backups of the iPhones that are compromised, Kaspersky employed the Mobile Verification Toolkit.
Enabling them to analyze the attack process and malware’s behavior on infected iPhones, which otherwise would be impossible.
Despite the malware’s effort to erase evidence of its presence on devices, specific indications of infection persist.
These include alterations to system files that hinder the installation of iOS updates, abnormal data consumption, and the introduction of outdated libraries into the system.
Upon thorough analysis, it was discovered that the initial indications of infection date back to 2019.
Remarkably, the most recent iOS version to be affected by this malicious toolset is 15.7, showcasing the persistence and adaptability of the threat.
During the iMessage transmission, the attachment remains encrypted and is retrieved via HTTPS, making it challenging to detect any explicit indicators.
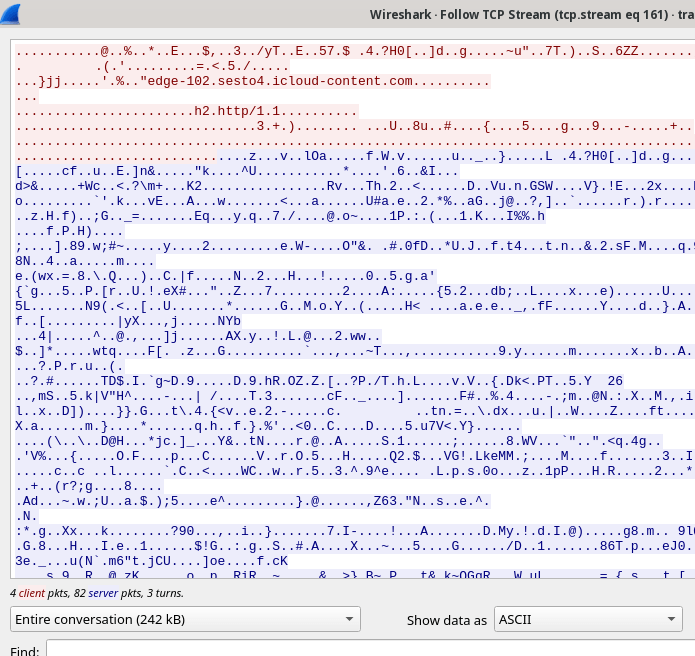
However, a potential implicit indicator lies in the size of the downloaded data, which typically amounts to approximately 242 Kb.
By utilizing iMessage as the delivery channel, the exploit initiates a process of code execution on iOS devices by exploiting an undisclosed vulnerability.
This allows the attacker to retrieve further stages from their server, which may include exploits for privilege escalation.
In order to assist security administrators in identifying potential signs of exploitation on their devices, the security firm has furnished a comprehensive list of 15 domains linked to this malicious activity.
By cross-referencing these domains with historical DNS logs, admins can effectively investigate any indications of compromise.
Once the malware successfully escalates to root privileges, it acquires a comprehensive toolset capable of executing commands.
This toolset enables the collection of crucial system and user data, while also facilitating the download of supplementary modules from the command and control (C2) server.
C&C Domains
Here below we have mentioned all the C&C domains:-
- addatamarket[.]net
- backuprabbit[.]com
- businessvideonews[.]com
- cloudsponcer[.]com
- datamarketplace[.]net
- mobilegamerstats[.]com
- snoweeanalytics[.]com
- tagclick-cdn[.]com
- topographyupdates[.]com
- unlimitedteacup[.]com
- virtuallaughing[.]com
- web-trackers[.]com
- growthtransport[.]com
- anstv[.]net
- ans7tv[.]net
Struggling to Apply The Security Patch in Your System? –
Try All-in-One Patch Manager Plus



