In a sophisticated cyberattack that unfolded over 29 days, cybersecurity analysts have meticulously traced the steps of threat actors from the initial infection with IcedID malware to the eventual deployment of Dagon Locker ransomware.
The detailed account of this cyber intrusion provides a chilling example of how quickly and stealthily cybercriminals can compromise an organization’s network and cause significant damage.
The Initial Breach: IcedID Phishing Campaign
The attack began with a phishing campaign that cleverly distributed IcedID, a notorious banking trojan, through emails containing malicious links. Victims who clicked on these links were directed to a fraudulent website designed to mimic an Azure download portal, where they were prompted to download a JavaScript file that initiated the malware infection.
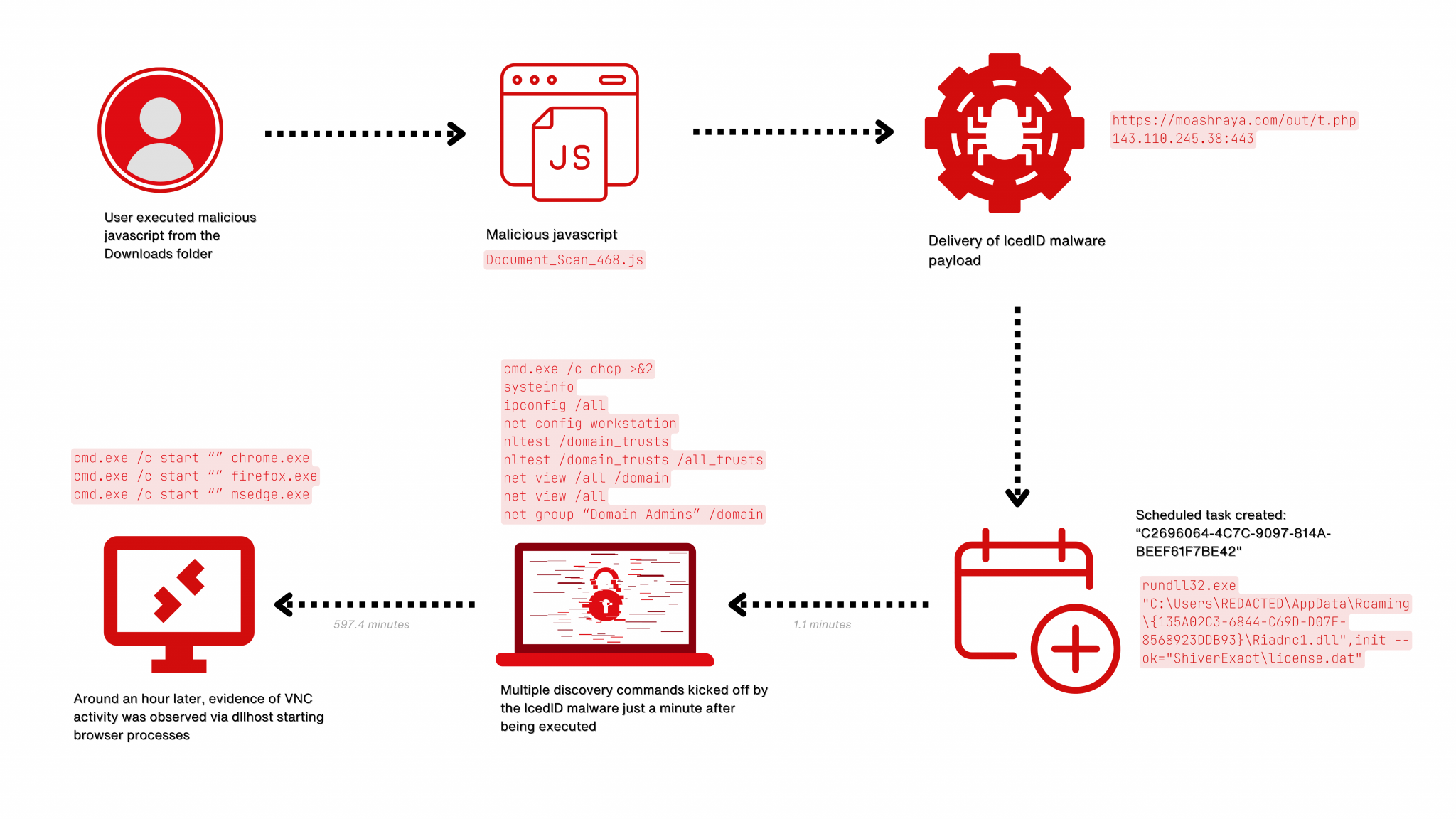
Once the IcedID malware was installed, it wasted no time establishing persistence and a command and control (C2) connection.
Within 30 hours, the malware downloaded and executed a Cobalt Strike beacon, a tool attackers frequently use to maintain a foothold in the network and facilitate lateral movement.
The attackers demonstrated their prowess by leveraging a suite of tools, including a custom PowerShell script known as AWScollector, to conduct discovery operations, move laterally, and exfiltrate data.
They also used Group Policy to distribute Cobalt Strike beacons to specific privileged user groups, further entrenching themselves within the network.
Combat Email Threats with Phishing Simulations:Free Email Security Awareness Training -> Try Free Demo
The Deployment of Dagon Locker Ransomware
On the 29th day, the attackers prepared for their final act by staging the Dagon Locker ransomware file on a domain controller.

Using their custom AWScollector script, they deployed the ransomware via SMB to remote hosts, disabling services and deleting shadow copies to prevent data recovery.
The ransomware crippled the entire network and demanded payment to unlock the encrypted data.
This incident serves as a stark reminder of the sophistication and persistence of modern cyber threats.
The attackers’ use of many tools, including Rclone, Netscan, Nbtscan, AnyDesk, Seatbelt, Sharefinder, and AdFind, underscores the need for robust cybersecurity measures and constant vigilance.
Using AnyDesk, a legitimate remote desktop application, for lateral movement and creating new user accounts with administrative privileges highlights the attackers’ ability to blend in with normal network activity and evade detection.
The thorough timeline of the attack, from the initial phishing email to the deployment of ransomware, demonstrates the attackers’ methodical approach.
According to the difrreport research, it also emphasizes the importance of early detection and response. The Time to Ransomware (TTR) of 29 days indicates that organizations may have a window of opportunity to detect and mitigate such threats before they escalate to full-blown ransomware deployment.
Lessons Learned and Recommendations
Cybersecurity experts recommend that organizations:
- Train employees to recognize and report phishing attempts.
- Implement multi-factor authentication to reduce the impact of credential theft.
- Keep all systems patched and up-to-date to prevent exploitation of known vulnerabilities.
- Employ endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to identify and respond to malicious activities.
- Regularly back up data and ensure backups are stored securely and inaccessible from the network.
The journey from IcedID infection to Dagon Locker ransomware deployment is a cautionary tale for organizations worldwide.
As cybercriminals continue to refine their tactics and tools, the need for comprehensive cybersecurity strategies has never been greater.
Organizations can better prepare to defend against and respond to the evolving threat landscape by understanding the methods used in such attacks.
Is Your Network Under Attack? - Read CISO’s Guide to Avoiding the Next Breach - Download Free Guide
Indicators of Compromise
Atomic
IcedID
143.110.245[.]38:443
159.89.124[.]188:443
188.114.97[.]7:443
151.236.9[.]176:443
159.223.95[.]82:443
194.58.68[.]187:443
87.251.67[.]168:443
151.236.9[.]166:443
rpgmagglader[.]com
ultrascihictur[.]com
oopscokir[.]com
restohalto[.]site
ewacootili[.]com
magiraptoy[.]com
fraktomaam[.]com
patricammote[.]com
moashraya[.]comCobalt Strike
23.159.160[.]88
45.15.161[.]97
51.89.133[.]3
winupdate.us[.]to
Computed
Document_Scan_468.js 0d8a41ec847391807acbd55cbd69338b 5066e67f22bc342971b8958113696e6c838f6c58 f6e5dbff14ef272ce07743887a16decbee2607f512ff2a9045415c8e0c05dbb4 license.dat bff696bb76ea1db900c694a9b57a954b ca10c09416a16416e510406a323bb97b0b0703ef 332afc80371187881ef9a6f80e5c244b44af746b20342b8722f7b56b61604953 Riadnc1.dll a144aa7a0b98de3974c547e3a09f4fb2 34c9702c66faadb4ce90980315b666be8ce35a13 9da84133ed36960523e3c332189eca71ca42d847e2e79b78d182da8da4546830 magni.w 7e9ef45d19332c22f1f3a316035dcb1b 4e0222fd381d878650c9ebeb1bcbbfdfc34cabc5 839cf7905dc3337bebe7f8ba127961e6cd40c52ec3a1e09084c9c1ccd202418e magni.w.bat b3495023a3a664850e1e5e174c4b1b08 38cd9f715584463b4fdecfbac421d24077e90243 65edf9bc2c15ef125ff58ac597125b040c487640860d84eea93b9ef6b5bb8ca6 update.dll 628685be0f42072d2b5150d4809e63fc 437fe3b6fdc837b9ee47d74eb1956def2350ed7e a0191a300263167506b9b5d99575c4049a778d1a8ded71dcb8072e87f5f0bbcf
