A new ransomware named KageNoHitobito has been targeting Windows users across various countries.
It encrypts their data and demands a ransom through sophisticated means.
This article delves into the mechanics of the KageNoHitobito ransomware and its attack methodology and provides a brief overview of another emerging threat, the DoNex ransomware.
Infection Vector/Victimology
The KageNoHitobito ransomware has been identified in multiple countries, including Chile, China, Cuba, Germany, Iran, Lithuania, Peru, Romania, Sweden, Taiwan, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
Is Your Network Under Attack? - Read CISO’s Guide to Avoiding the Next Breach - Download Free Guide
The widespread distribution suggests that the ransomware may have been disseminated through file-sharing services, masquerading as legitimate software or game cheats.
Thus, users were tricked into downloading and executing malicious files.
According to a recent report by Fortinet, KageNoHitobito ransomware is targeting Windows users across the globe.
The attack is designed to exploit Windows system vulnerabilities, leading to compromised security and potential data loss.
Integrate ANY.RUN in Your Company for Effective Malware Analysis
Are you from SOC, Threat Research, or DFIR departments? If so, you can join an online community of 400,000 independent security researchers:
- Real-time Detection
- Interactive Malware Analysis
- Easy to Learn by New Security Team members
- Get detailed reports with maximum data
- Set Up Virtual Machine in Linux & all Windows OS Versions
- Interact with Malware Safely
If you want to test all these features now with completely free access to the sandbox:
Attack Method
KageNoHitobito is designed to encrypt files on local drives, appending a “.hitobito” extension to the encrypted files.
It strategically avoids encrypting critical system files such as .dat, .dll, .exe, .ini, .log, and .sys to ensure the system remains operational, presumably to facilitate communication with the victim for ransom negotiations.
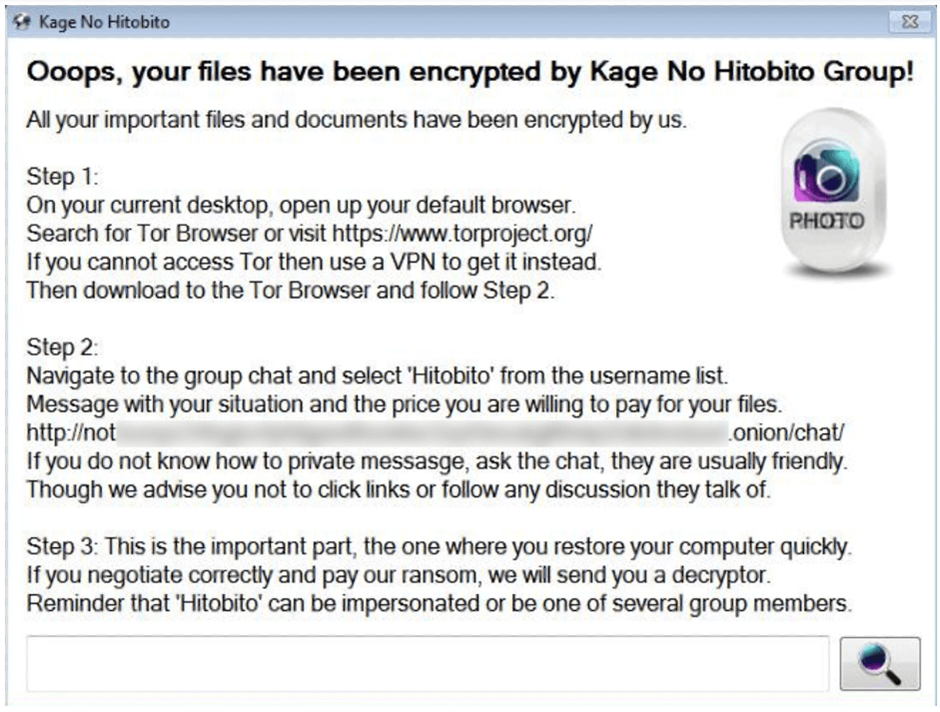
The ransomware displays a ransom note on the victim’s desktop and drops a text-based note, urging victims to contact the attackers via a TOR site using the AbleOnion chat platform.
Interestingly, the chat platform does not seem dedicated solely to ransom negotiations, indicating a possible use of a public or shared platform to avoid detection.
DoNex Ransomware Overview
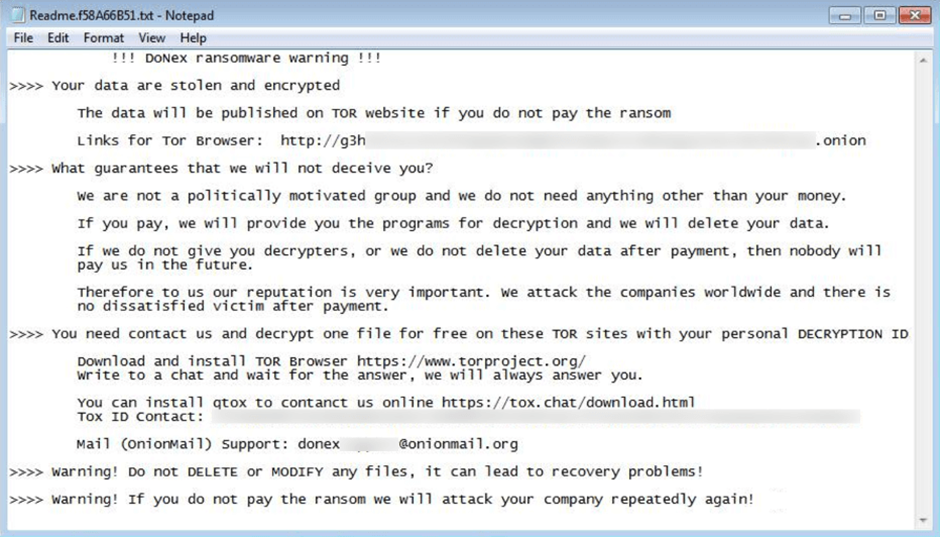
Parallel to the KageNoHitobito, another ransomware named DoNex has been making rounds since early March 2024.
Unlike KageNoHitobito, DoNex has a data leak site and has been reported to encrypt files on both local and network drives.
The ransomware is highly configurable, allowing it to adapt its operations based on the environment it infects.
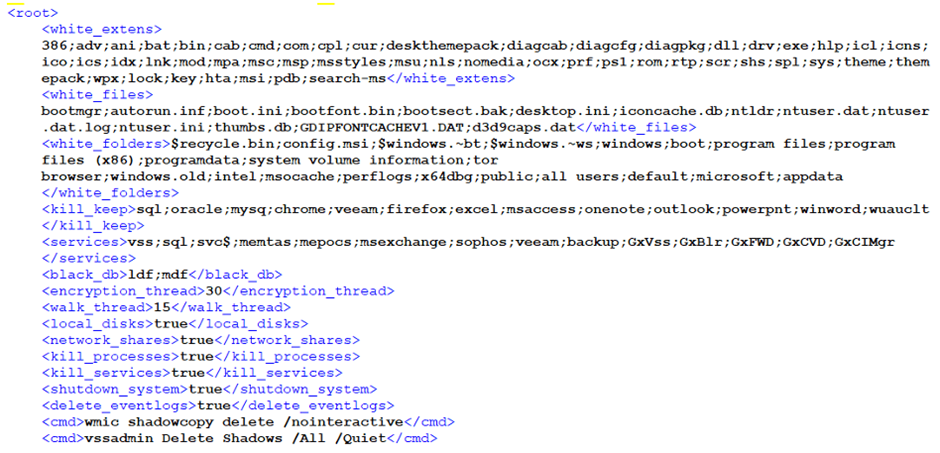
DoNex avoids encrypting a wide range of file extensions and specific critical system folders, ensuring the system’s usability post-infection.
It also terminates various processes and services, enhancing its ability to encrypt files without interference.
The ransom note of DoNex shares similarities with another ransomware, DarkRace, suggesting a possible link between the two in terms of their origin or the threat actors behind them.
Both KageNoHitobito and DoNex ransomware represent significant threats to global cybersecurity.
Their sophisticated attack methods and international reach highlight the need for increased vigilance and robust cybersecurity measures among users and organizations worldwide.
IOCs
| SHA2 | Note |
| 8939bfe20bc6476806d22c8edfcaba5c36f936b893b3de1c847558502654c82f | Hitobito ransomware |
| 1940fcdb2561c2f7b82f6c44d22a9906e5ffec2438d5dadfe88d1608f5f03c33 | |
| 506e8753dd5ca1c8387be32f26367e26f242b7c65e61203f7f926506c04163aa | |
| 8a10e0dc4994268ea33baecd5e89d1e2ddabef30afa09961257a4329669e857a | |
| bec9d2dcd9565bb245f5c8beca4db627390bcb4699dd5da192cc8aba895e0e6a | |
| 0adde4246aaa9fb3964d1d6cf3c29b1b13074015b250eb8e5591339f92e1e3ca | DoNex ransomware |
| 6d6134adfdf16c8ed9513aba40845b15bd314e085ef1d6bd20040afd42e36e40 | |
| b32ae94b32bcc5724d706421f915b7f7730c4fb20b04f5ab0ca830dc88dcce4e | |
| 74b5e2d90daaf96657e4d3d800bb20bf189bb2cf487479ea0facaf6182e0d1d3 | DarkRace ransomware(predecessor of DoNex) |
| 0e60d49a967599fab179f8c885d91db25016be996d66a4e00cbb197e5085efa4 |
Combat Email Threats with Easy-to-Launch Phishing Simulations: Email Security Awareness Training -> Try Free Demo