A coordinated and new malware campaign is exploiting the popular developer platform, GitHub. The target? Professionals in IT administration, cybersecurity, and open-source intelligence (OSINT). This is according to a detailed research report by Morphisec Threat Labs on a previously unknown threat, dubbed PyStoreRAT.
For your information, PyStoreRAT is a Remote Access Trojan, which is a type of malicious program that gives an attacker secret, long-term control over a victim’s computer. Researchers observed that this campaign is different because it involves careful planning and uses tools created by Artificial Intelligence (AI) to appear legitimate.
The AI-Assisted Supply Chain Attack
The preemptive cyber defence firm Morphisec’s investigation revealed that the attackers’ smart strategy began over the last several months by reactivating dormant GitHub accounts, some of which had been inactive for years.
These accounts then started posting seemingly authentic, polished projects that were created using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to build immediate trust. These projects included useful software like OSINT tools, crypto trading bots (DeFi bots), and AI chat wrappers (GPT wrappers).
These convincing projects/repositories were so well-made that several quickly climbed high on GitHub’s trending lists. Only after gaining this traction and trust did the criminals introduce subtle code updates, disguised as simple ‘maintenance, to plant the PyStoreRAT backdoor.
PyStoreRAT- A Multi-Purpose, Evasive Threat
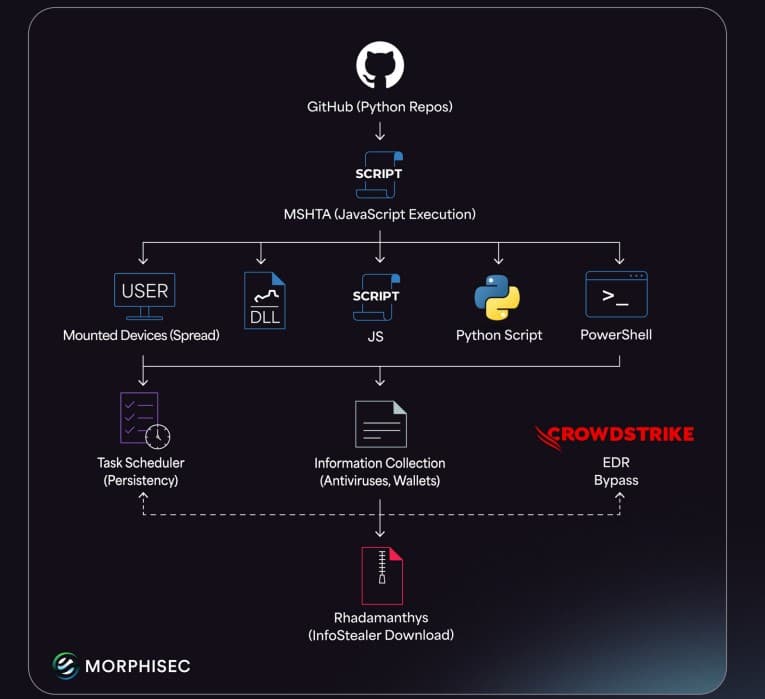
Further investigation revealed that PyStoreRAT is designed for stealth and flexibility. It is multi-functional as it performs a full profile of the victim’s computer and can deploy other types of harmful software, including the infamous data-stealing malware like the Rhadamanthys stealer and Python Loader.
It is worth noting that the malware is highly adaptive. According to Morphisec’s research, it even switches its launch method when it detects certain security software like CrowdStrike Falcon or products from CyberReason and ReasonLabs to reduce its visibility. Moreover, the malware can spread through portable storage devices like USB drives and dynamically pulls new components directly from its operators.
Additionally, researchers found a circular, rotating system of control servers for the malware, which helps it quickly update its commands and makes it much harder to shut down. The presence of Russian-language strings in the code, such as the word “СИСТЕМА” (which means SYSTEM), suggests the overall operation is far “beyond typical GitHub-malware noise,” Morphisec’s malware researcher Yonatan Edri explained in the blog post shared with Hackread.com.
List of Malicious GitHub Repositories
Here is a list of all malicious GitHub repositories used in the campaign. The good news is that most of the repositories have been deleted by GitHub. The bad news is that a few are still available.
- https://github.com/setls/HacxGPT
- https://github.com/turyems/openfi-bot
- https://github.com/bytillo/spyder-osint
- https://github.com/gonflare/KawaiiGPT
- https://github.com/tyreme/spyder-osint
- https://github.com/gumot0/spyder-osint
- https://github.com/rizvejoarder/SoraMax
- https://github.com/Zeeeepa/spyder-osint
- https://github.com/aiyakuaile/easy_tv_live
- https://github.com/WezRyan/spyder-osint
- https://github.com/Zeeeepa/spyder-osint2
- https://github.com/Metaldadisbad/HacxGPT
- https://github.com/Manojsiriparthi/spyder-osint
- https://github.com/xhyata/crypto-tax-calculator
- https://github.com/turyems/Pharos-Testnet-bot
- https://github.com/adminlove520/VulnWatchDog
- https://github.com/shivas1432/sora2-watermark-remover
This blending of AI-generated legitimacy, social engineering, cloud resilience, and adaptive execution is being called an “evolutionary step” in the world of online threats, making traditional security measures “fundamentally unreliable.” That’s why Morphisec emphasises that defenders responsible for safeguarding developer environments or sensitive data must understand how this malware works to safeguard systems
