The developers of the GoAnywhere MFT file transfer solution are warning customers of zero-day remote code execution vulnerability on exposed administrator consoles.
GoAnywhere is a secure web file transfer solution that allows companies to securely transfer encrypted files with their partners while keeping detailed audit logs of who accessed the files.
The GoAnywhere security advisory was first made public by reporter Brian Krebs, who posted a copy on Mastodon.
A customer who received the notification told BleepingComputer that this is affecting both the on-premise and SaaS implementations of GoAnywhere but we could not independently confirm this at this time.
According to the security advisory, the exploit requires access to the administrative console, which should not normally be exposed to the internet.
“A Zero-Day Remote Code Injection exploit was identified in GoAnywhere MFT,” warns the GoAnywhere security advisory.
“The attack vector of this exploit requires access to the administrative console of the application, which in most cases is accessible only from within a private company network, through VPN, or by allow-listed IP addresses (when running in cloud environments, such as Azure or AWS).”
As there is no patch currently available for the zero-day vulnerability, Fortra urges admins to apply the following mitigation:
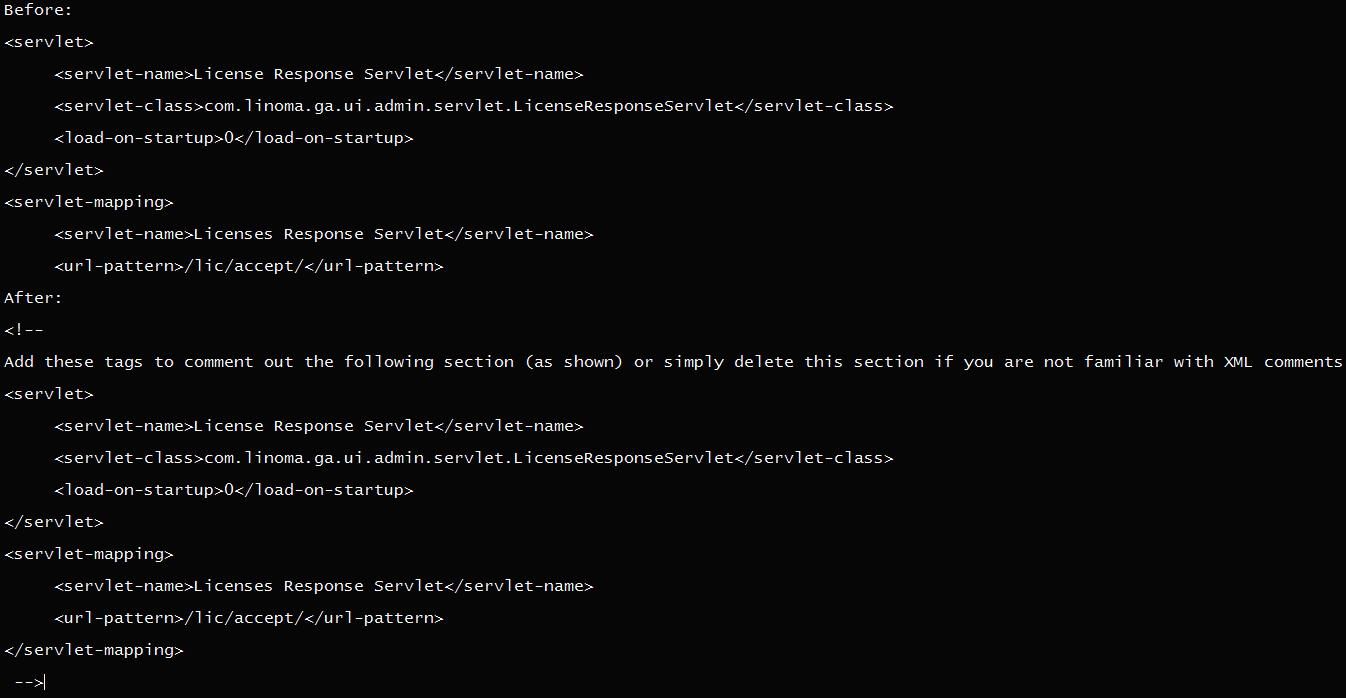
- On the file system where GoAnywhere MFT is installed, edit the file “[install_dir]/adminroot/WEB_INF/web.xml.”
- Find and remove (delete or comment out) the following servlet and servlet-mapping configuration in the screenshot below.
- Restart the GoAnywhere MFT application.
At this time, there’s no other way to mitigate the attacks, as Fortra has not yet made a security update available.
Fortra has also temporarily shut down its SaaS solution while they resolve the bug.
The company also recommends that Administrators perform an audit of their installations, including:
- Check to see if new, unknown admin accounts were created by the ‘system’ and if the “Admin Audit Log shows a non-existent or disabled super user creating this account.”
- Search the Administration log for activity (Reporting -> Audit Logs -> Administration). Search for anything created by root user.
Security professional Kevin Beaumont has performed a Shodan scan to determine how many GoAnywhere instances are exposed on the internet and found 1,008 servers, mainly in the United States.
However, Beaumont said that most admin consoles utilize ports 8000 and 8001, of which BleepingComputer only saw 151 exposed.
While the attack surface may appear limited, it’s important to note that large organizations use these products to transfer sensitive files with their partners.
BleepingComputer has identified local governments, healthcare companies, banks, energy firms, financial services companies, museums, and computer part manufacturers utilizing the GoAnywhere file transfer solution.
Hence, even a single breach leveraging GoAnywhere MFT’s zero-day flaw could leak sensitive information that could be used for extortion.
This exact scenario was seen in the 2021 hacks of Accellion FTA (File Transfer Appliance) by the Clop ransomware gang, which impacted many high-profile companies worldwide.
BleepingComputer has contacted Fortra to ask for more details about whether the attacks are actively exploited, and we will update this post as soon as we receive a response.
