A critical vulnerability in Ray, an open-source AI framework that is widely utilized across various sectors, including education, cryptocurrency, and biopharma.
This vulnerability, known as CVE-2023-48022, has been under active exploitation for the past seven months, allowing attackers to hijack computing power and leak sensitive data.
The Discovery of CVE-2023-48022: ShadowRay
Late in 2023, five unique vulnerabilities were disclosed to Anyscale, the developers of Ray, by cybersecurity entities Bishop Fox, Bryce Bearchell, and Protect AI.
Anyscale addressed four of these vulnerabilities in Ray version 2.8.1, but the fifth, CVE-2023-48022, remains disputed and unpatched.
The Oligo team has dubbed this vulnerability “ShadowRay” due to its ability to evade static scans and lead to significant breaches.
AI environments are goldmines for attackers due to the sensitive information they contain, such as private intellectual property, third-party tokens, and access to company databases.
The high-powered machines used for AI models are also prime targets for their computing power.
The Oligo research team has uncovered an active attack campaign that has put thousands of servers at risk.
Meet Ray: The Affected Framework
Ray is a unified framework designed to scale AI and Python applications.
Anyscale maintains it and has garnered significant attention, with 30K stars on GitHub.
Large organizations like Uber, Amazon, and OpenAI use Ray in production for its scalability and efficiency.

The Exploitation of Ray Clusters
The lack of authorization in Ray’s Jobs API has been a critical point of exploitation.
Attackers with network access to the dashboard can invoke arbitrary jobs on the remote host without authorization.

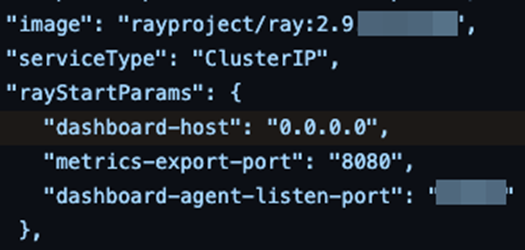

Ray’s official Kubernetes deployment guide [10] and Kuberay’s Kubernetes operator encourage people to expose the dashboard on 0.0.0.0:
This oversight has led to the compromise of numerous publicly exposed Ray servers, with attackers leveraging the flaw for cryptocurrency mining and data theft.
The collective value of the compromised machines is staggering, with the potential worth nearing a billion USD.
Attackers are drawn to these machines not only for the sensitive information they can extract but also for the high value of the GPUs, which are in short supply and expensive.

The Common Thread: Crypto Miners
Oligo Research has identified patterns in the compromised clusters, suggesting that the same attackers targeted them.
Crypto-mining campaigns have been leveraging ShadowRay to install miners and reverse-shells, with some attackers reaching the top 5% of miners in certain pools.

In light of these findings, organizations using Ray are urged to review their environments for exposure and analyze any suspicious activity.
For more detailed information on the vulnerabilities and the steps taken by Anyscale, readers can refer to the blog posts by Bishop Fox, Bryce Bearchell, and Protect AI.
Ray users must be aware of the security aspects and common pitfalls associated with the framework.
As the battle between functionality and security continues, the Ray incident serves as a stark reminder of the importance of vigilance in the digital age.
The disputed nature of CVE-2023-48022 has not only highlighted the complexities of software development but also the critical need for robust security measures in protecting valuable AI infrastructure.
Stay updated on Cybersecurity news, Whitepapers, and Infographics. Follow us on LinkedIn & Twitter
