Kali Linux has released version 2024.2, the first version of 2024, with eighteen new tools and fixes for the Y2038 bug.
Kali Linux is a distribution created for cybersecurity professionals and ethical hackers to perform penetration testing, security audits, and research against networks.
As is typical for the year’s first version, the Kali Team has released new visual elements, including wallpapers and updates to the boot menu and login display.
Eighteen new tools in Kali Linux 2024.2
What’s a new Kali release without new tools toys to play with?
Kali 2024.2 doesn’t disappoint, with eighteen new tools added in this release:
- autorecon – Multi-threaded network reconnaissance tool
- coercer – Automatically coerce a Windows server to authenticate on an arbitrary machine
- dploot – Python rewrite of SharpDPAPI
- getsploit – Command line utility for searching and downloading exploits
- gowitness – Web screenshot utility using Chrome Headless
- horst – Highly Optimized Radio Scanning Tool
- ligolo-ng – Advanced, yet simple, tunneling/pivoting tool that uses a TUN interface
- mitm6 – pwning IPv4 via IPv6
- netexec – Network service exploitation tool that helps automate assessing the security of large networks.
- pspy – Monitor Linux processes without root permissions
- pyinstaller – Converts (packages) Python programs into stand-alone executables.
- pyinstxtractor – PyInstalller Extractor
- sharpshooter – Payload Generation Framework
- sickle – Payload development tool
- snort – Flexible Network Intrusion Detection System
- sploitscan – Search for CVE information
- vopono – Run applications through VPN tunnels with temporary network namespaces
- waybackpy – Access Wayback Machine’s API using Python
Kali says they did not have time to get Linux Kernel 6.8 included, which was released on March 10, but will be included in version 2024.3.
Year 2038 bug fixes
Similar to the Y2K bug, the ‘year 2038 problem’ (aka Y2038 and Y2K38) will cause the time to switch to 1901-12-13 20:45:52 after reaching 2038-01-19 03:14:08 UTC on Linux systems when UNIX timestamps are stored in a 32-bit time_t integer variable.
To fix this, compilers and libraries switched to the larger 64-bit time_t integers that properly store timestamps when we reach 2038. However, this requires applications and libraries using the previous 32-bit variables to be recompiled so as to not cause issues.
“To prevent the Year 2038 issue, the size for the time_t type had to be changed to be 64-bit, on those architectures where it was 32-bit. For Kali Linux, that means the two 32-bit ARM architectures that we support: armhf and armel. These architectures are used mainly for ARM images (eg. Raspberry Pi) and a few NetHunter images. Note that the i386 architecture (ie. legacy PC) didn’t change: this architecture still will have a 32-bit time_t type, and that will not change. Kali has always treated ARM platform as a first-class citizen.”
❖ The Kali Team
Kali says they have now finished its t64 transition, meaning that all Kali users should perform a full upgrade to receive the new updated packages.
New desktop changes
This release introduces Gnome 46, with all themes and extensions updated to support the new version.
The developers have also updated the Xfce desktop with new stability and performance fixes.
Source: Kali
How to get Kali Linux 2024.2
To start using Kali Linux 2024.2, you can upgrade your existing installation, select a platform, or directly download ISO images for new installs and live distributions.
For those updating from a previous version, you can use the following commands to upgrade to the latest version.
echo "deb http://http.kali.org/kali kali-rolling main contrib non-free non-free-firmware" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list
sudo apt update && sudo apt -y full-upgrade
cp -vrbi /etc/skel/. ~/
[ -f /var/run/reboot-required ] && sudo reboot -f
If you are running Kali on the Windows Subsystem for Linux, upgrade to WSL2 for a better experience, including the ability to use graphical apps.
You can check the WSL version used by Kali with the ‘wsl -l -v’ command in a Windows command prompt.
Once done upgrading, you can check if the upgrade was successful by using the following command:
grep VERSION /etc/os-release
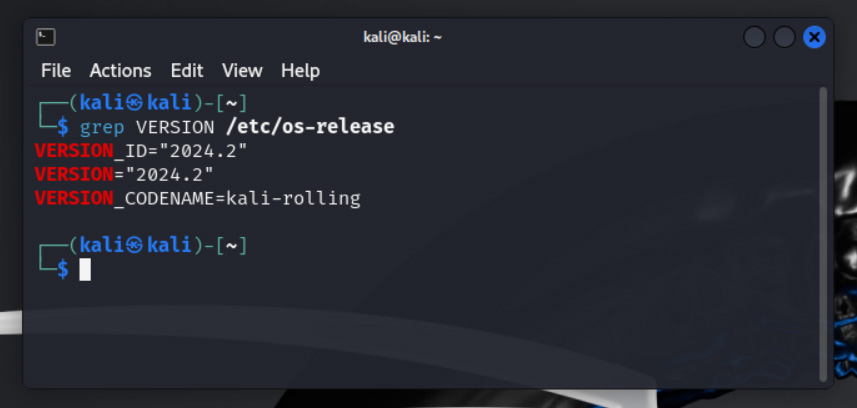
Source: BleepingComputer
You can view the complete changelog for Kali 2024.2 on Kali’s website.
