A critical vulnerability has been identified in the Mobile Security Framework (MobSF) that allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into the system.
This vulnerability, CVE-2024-53999 is a Stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) flaw found in the “Diff or Compare” functionality, which occurs due to improper handling of file uploads with script-laden filenames.
Details of the Vulnerability
The vulnerability was discovered in MobSF version 4.2.8 in Github, where the application allows users to upload files with scripts embedded in the filename parameter.

Specifically, the issue arises because the upload feature permits filenames containing special characters such as <, >, /, and “. Such oversights make it possible for a malicious user to upload a script file and set its name to a script value, which the server accepts without validation.
Leveraging 2024 MITRE ATT&CK Results for SME & MSP Cybersecurity Leaders – Attend Free Webinar
This oversight can potentially be mitigated by implementing stricter filename validation. By restricting file uploads to filenames containing only whitelisted characters—such as A-Z, 0-9, and specific special characters like – or _ that are permitted by business requirements—this risk could be significantly reduced.
Proof of Concept (PoC)
To illustrate this vulnerability, a proof of concept was created with the following steps:
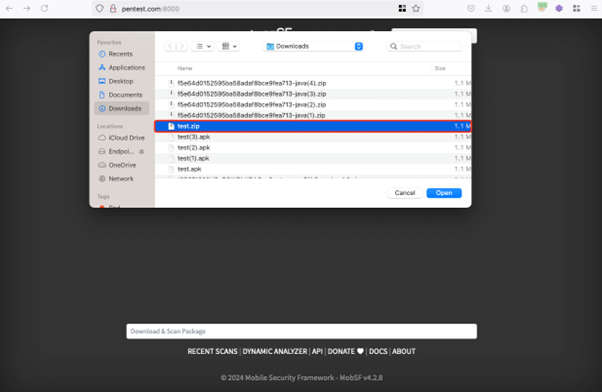
- Use of Intercepting Proxy: On MobSF version 4.2.8, the “Unload & Analyze” button was clicked, and a file named test.zip was uploaded. During this process, an intercepting proxy tool was used to change the value of the filename parameter from test.zip to
test.zip.

- Successful Upload: The altered filename was accepted by the server, and the file was uploaded successfully.

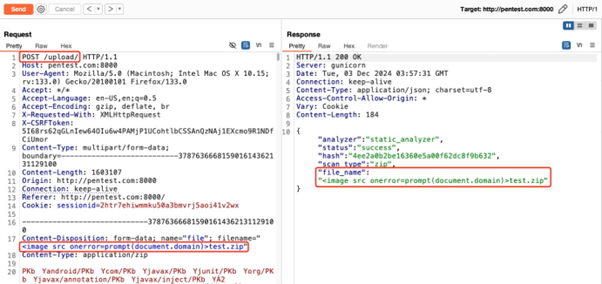
- Script Execution: Upon accessing /recent_scans/, the file
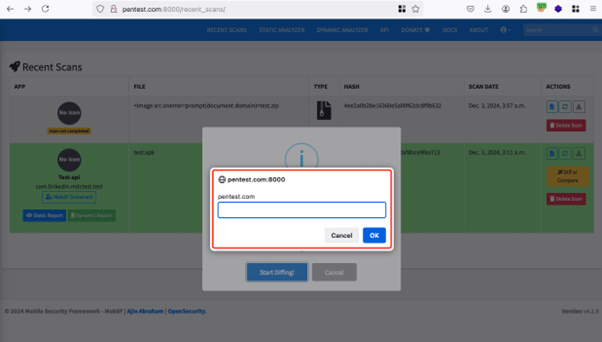
test.zip appeared in the list. Clicking on the “Differ or Compare” button and selecting this file led to the execution of JavaScript embedded in the filename within the web browser.

The impact of this vulnerability is significant. By allowing a malicious script to be stored in the system via the filename parameter, attackers can access sensitive information belonging to other users or administrators during the comparison process.

This flaw not only compromises data confidentiality but also poses a persistent threat as the injected script remains stored in the system.
The MobSF team is urged to implement immediate fixes by validating and sanitizing filename inputs to prevent such vulnerabilities.
In the meantime, users are advised to exercise caution and apply any patches or updates released by the MobSF developers to mitigate these security risks.
Analyse Advanced Malware & Phishing Analysis With ANY.RUN Black Friday Deals : Get up to 3 Free Licenses.
